-
Research Article

-
Urban-scaled EnergyPlus Simulation Based on GIS to Construct Database for Supporting Development of Building Shading Indicator
건물 음영 지표 개발용 데이터베이스 구축을 위한 GIS 기반 도시 단위 EnergyPlus 시뮬레이션
-
Dong-Hyuk Yi, Deuk-Woo Kim
이동혁, 김덕우
- As widely acknowledged, building energy use is strongly interplayed with neighboring buildings, such as shading or incident solar radiation. In other words, …
- As widely acknowledged, building energy use is strongly interplayed with neighboring buildings, such as shading or incident solar radiation. In other words, it is important to investigate building energy characteristics, not by a sole building but with a group of buildings. In this regard, the authors suggest the process of the urban-scaled building simulation using the geographic information system (GIS) to build the database that reflects the shading and the solar radiation that enter the building surface and is helpful for the development of building shading indicator. The GIS is a database that combines the geometric information of buildings as well as the properties of both buildings and the city. In this study, EnergyPlus was chosen as a dynamic building simulation tool, and the comprehensive process including gathering model information, customizing building footprint data, generating models, executing simulations, and organizing the urban-scaled building surface database. - COLLAPSE
-
Urban-scaled EnergyPlus Simulation Based on GIS to Construct Database for Supporting Development of Building Shading Indicator
-
Research Article
-
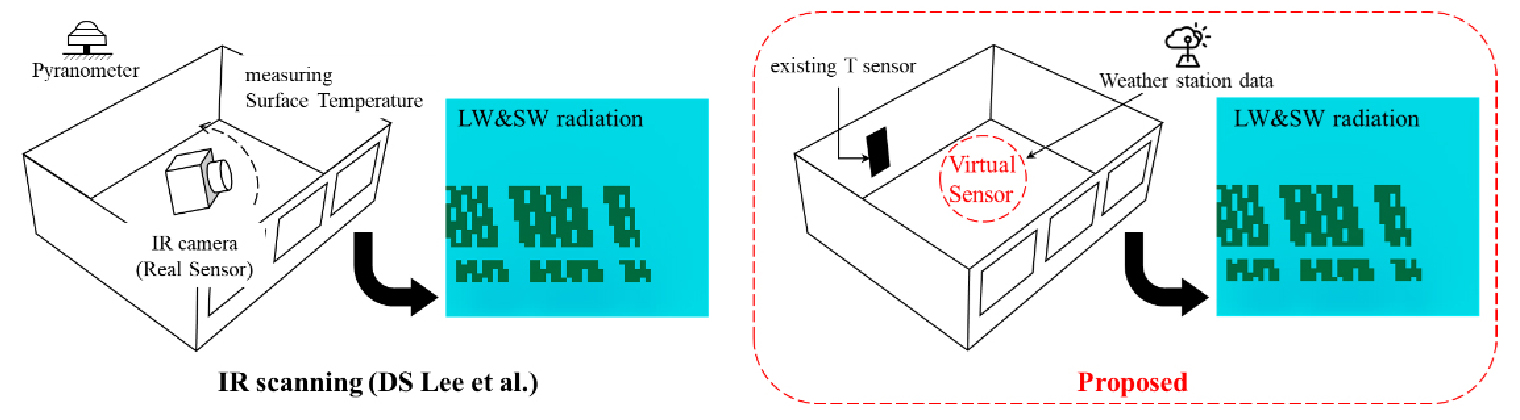
Real-time Prediction of Mean Radiant Temperature through Developed a Virtual Sensor Model using Existing Sensors
가상센서 모델 개발을 통한 건물 기존 온도 센서 활용 평균복사온도 실시간 예측
-
Hye-Jin Shin, Dong-Seok Lee
신혜진, 이동석
- The mean radiant temperature (MRT) is a critical factor influencing approximately half of the thermal comfort experienced by occupants. However, existing methods …
- The mean radiant temperature (MRT) is a critical factor influencing approximately half of the thermal comfort experienced by occupants. However, existing methods for measuring MRT have not been employed due to the physical limitations of the measuring equipment. This study aims to develop a virtual sensor model for predict MRT applicable in existing buildings without the need for additional sensor installations. To achieve this, experiment was conducted. Simplified resistance-capacity (RC) model was applied for building model. Using particle swarm optimization (PSO), R and C values were obtained to predict indoor surface temperatures. Finally, real-time MRT spatial distribution was predicted using the derived surface temperatures, and the outcomes were thoroughly discussed. The result of this study indicates the practical applicability of the MRT prediction model in occupied buildings. - COLLAPSE
-
Real-time Prediction of Mean Radiant Temperature through Developed a Virtual Sensor Model using Existing Sensors
-
Research Article
-
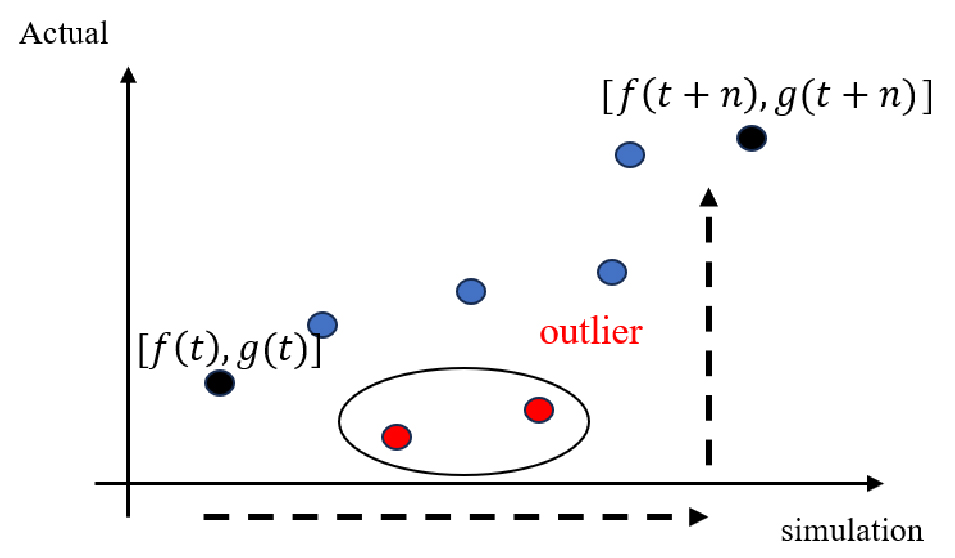
Anomaly Detection Algorithm Based on Hybrid Model for Establishing Appropriate Energy Baseline
적정 에너지 베이스라인 구축을 위한 하이브리드 모델 기반 이상값 검출 알고리즘
-
Tae-Kyu Lee, Jeong-Uk Kim
이태규, 김정욱
- This study explores the importance of establishing an appropriate energy baseline for the energy management of buildings and building complexes. The energy …
- This study explores the importance of establishing an appropriate energy baseline for the energy management of buildings and building complexes. The energy baseline serves as a benchmark for assessing a building’s energy consumption and accurately measuring the effects of energy-saving measures. With many buildings using energy inefficiently, accurately setting an energy baseline presents challenges. This research emphasizes the necessity of continuously monitoring a building’s energy consumption to establish a sustainable energy management strategy. The proper setting and management of an energy baseline play a crucial role in assessing the effectiveness of energy demand management projects. The study demonstrates that the energy baseline varies according to energy consumption behavior, revealing up to a 28% daily discrepancy in estimated energy baseline through the detection of anomaly data. These findings suggest difficulties in accurately determining an energy baseline, yet underline the need for appropriate criteria for judgment and the significance of constructing a proper baseline for accurately calculating the energy-saving effects from a demand management perspective. Future research aims to develop additional algorithms for analyzing energy consumption behavior and detecting anomalous data. - COLLAPSE
-
Anomaly Detection Algorithm Based on Hybrid Model for Establishing Appropriate Energy Baseline
-
Research Article
-
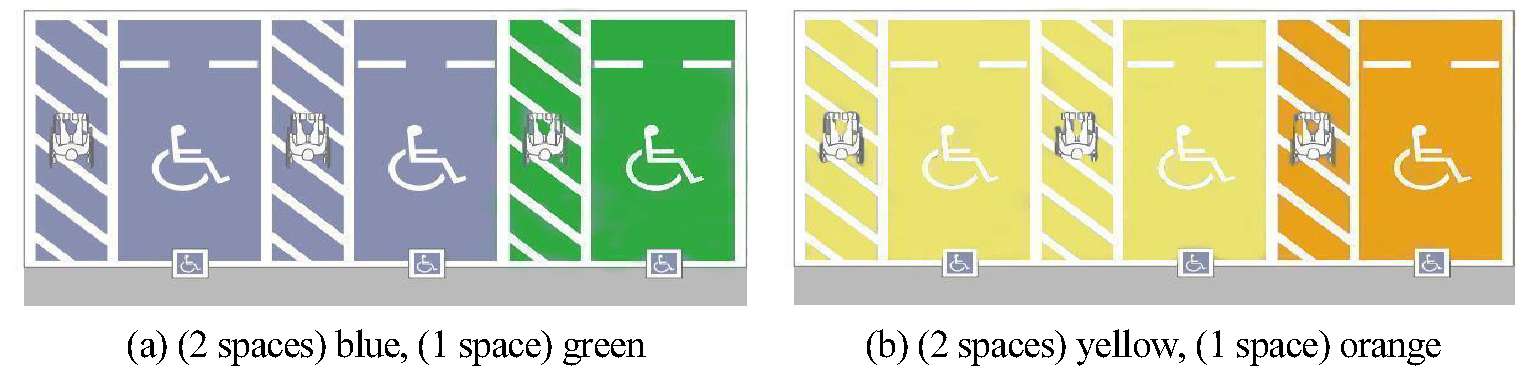
A Study on the Use Status and Efficient Use of Parking Lot for the Disabled
장애인 주차장의 사용실태와 효율적 이용에 대한 연구
-
Ju-Hye Yoon, Hong-Su Yun, Chang-Ho Choi
윤주혜, 윤홍수, 최창호
- This study shows that parking spaces can be secured when operated and utilized flexibly by increasing the utilization of parking spaces for …
- This study shows that parking spaces can be secured when operated and utilized flexibly by increasing the utilization of parking spaces for the disabled to solve parking difficulties. As the parking problem becomes serious, it is necessary to find out whether it is operating properly when looking at parking areas for the disabled that are often empty. Therefore, based on the above background, the usage status survey was conducted mainly in Nowon-gu, Seoul, and the purpose of this study is to provide directions for resolving parking problems and resolving inconveniences through the designation of parking areas for disabled people as required designated areas and flexible operation of parking hours available to the general public. - COLLAPSE
-
A Study on the Use Status and Efficient Use of Parking Lot for the Disabled
-
Research Article

-
A Study on the Economic Value of the Efficient Use of Parking Areas for the Disabled in Seoul
서울시 장애인 전용주차구역의 효율적 이용에 따른 경제적 가치에 관한 연구
-
Ju-Hye Yoon, Hong-Su Yun, Chang-Ho Choi
윤주혜, 윤홍수, 최창호
- In this study, to resolve the parking shortage in Seoul, a plan for the efficient operation of parking areas for the disabled …
- In this study, to resolve the parking shortage in Seoul, a plan for the efficient operation of parking areas for the disabled with great economic value was presented and the economic value of parking areas for the disabled was shown. The results of the survey on the current status of parking areas for the disabled were 21.25%, which was set higher than the average usage rate to minimize the inconvenience of the disabled, and 25% of them, which is higher than the average usage rate, were designated as essential areas for the disabled. Excluding 25% of them, 75% of them were efficiently operated, showing economic conversion values. Parking areas for the disabled occupy about 16.5 m² per parking space, and if these areas of great economic value are used, the cost of additional parking lot construction and carbon dioxide emission permits due to material production can be reduced. - COLLAPSE
-
A Study on the Economic Value of the Efficient Use of Parking Areas for the Disabled in Seoul
-
Research Article
-
Research Article
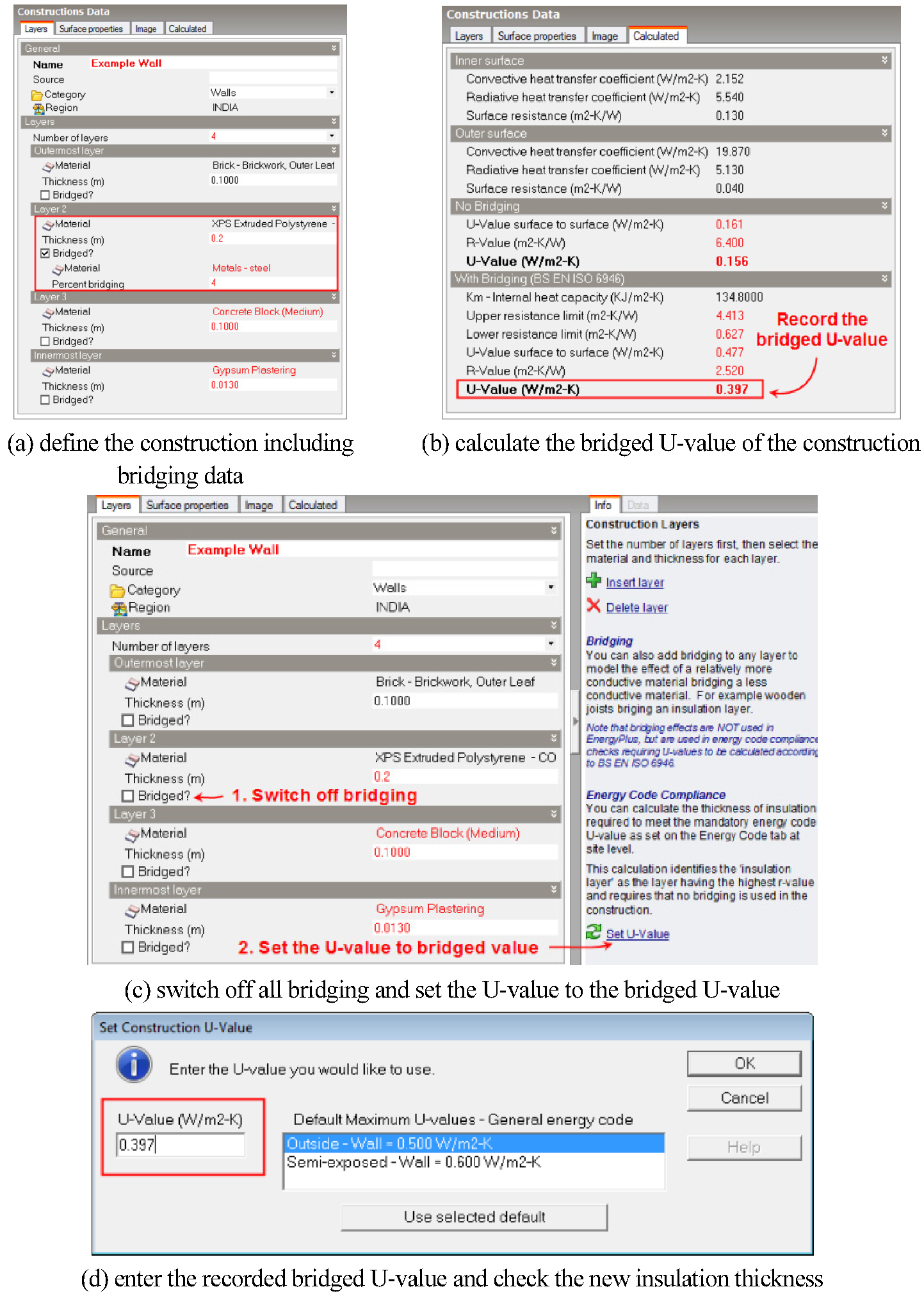
-
Evaluation of Thermal Bridging Effect Modeling Method in Building Energy Simulation Using DesignBuilder Program
DesignBuilder 프로그램을 이용한 건물에너지 해석에서 열교 영향 모델링 방법 평가
-
Bo-Hye Choi, Seung-Yeong Song
최보혜, 송승영
- The purpose of this study was to compare of results according to thermal bridging modeling method in building energy simulation using DesignBuilder …
- The purpose of this study was to compare of results according to thermal bridging modeling method in building energy simulation using DesignBuilder program. To model the thermal bridging effect in the DesignBuilder program, the effective U-factor and the heat transfer coefficient through linear and point thermal bridges were calculated and reflected through a three-dimensional heat transfer analysis. In the former case, the effect of thermal bridges is approximated by increasing or decreasing the thickness of the insulation only in the exterior wall configuration, while in the latter case, the effect of linear and point thermal bridges can be considered together by subtracting the heat flow rate through non-thermal bridges from the total heat flow rate. The method reflecting the heat transfer coefficient through the linear and point thermal bridges results in 13.9 to 19.6% greater annual heating and cooling energy use than the method reflecting the effective U-factor, and the savings for the base case and alternatives are similar for both methods. - COLLAPSE
-
Evaluation of Thermal Bridging Effect Modeling Method in Building Energy Simulation Using DesignBuilder Program
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of Korean Institute of Architectural Sustainable Environment and Building Systems
Journal of Korean Institute of Architectural Sustainable Environment and Building Systems
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of Korean Institute of Architectural Sustainable Environment and Building Systems
Journal of Korean Institute of Architectural Sustainable Environment and Building Systems











