-
Research Article
-
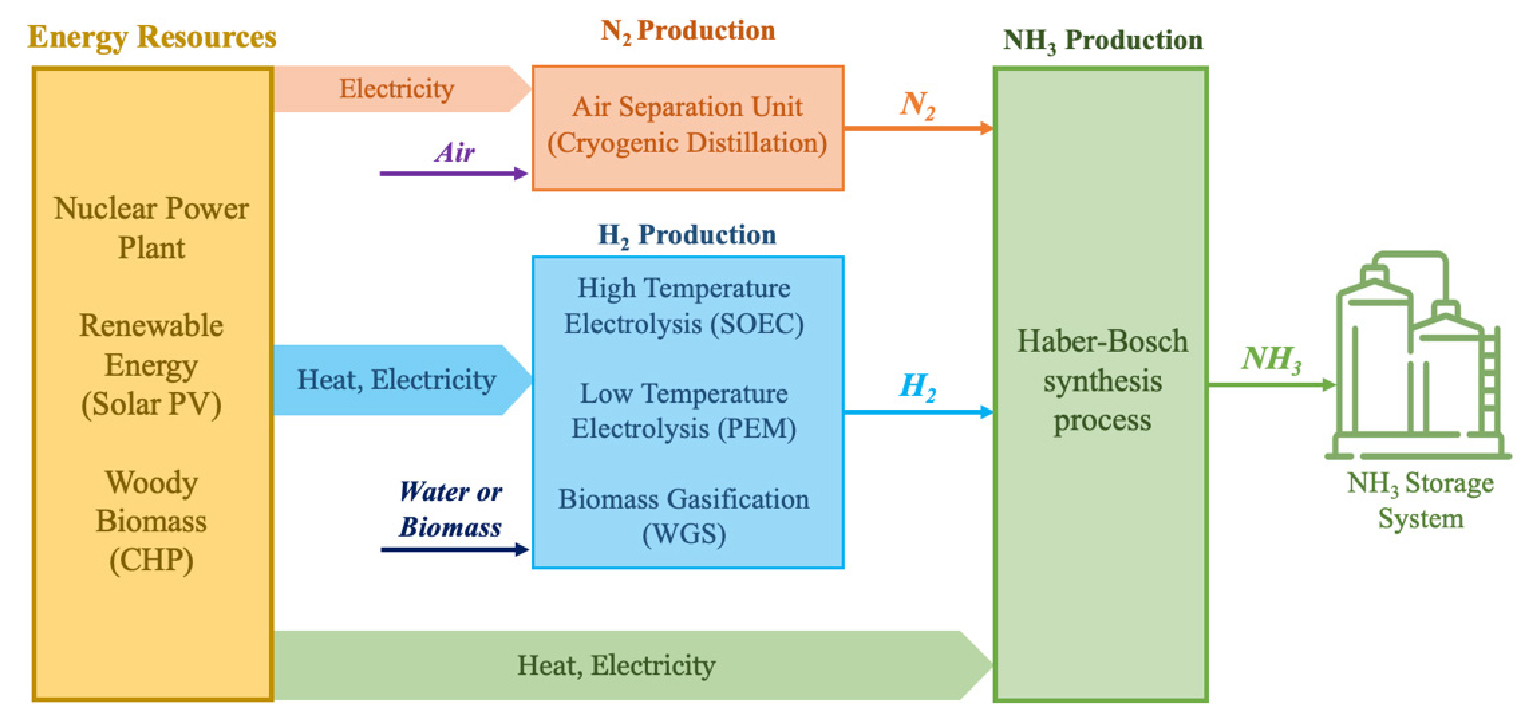
Comparative Techno-Economic Analysis of Hydrogen Production Process Facility and Renewable Energy for Green Ammonia
그린 암모니아를 위한 수소생산 공정설비와 재생에너지 기술-경제적 비교 분석
-
Kim, Ji-Ho, Yoshioka, Takuyuki, Kim, Jee-Young, Gwon, Min-Ji, Kim, Hyun-Bae
김지호, 요시오카 타쿠유키, 김지영, 권민지, 김현배
-
Comparative Techno-Economic Analysis of Hydrogen Production Process Facility and Renewable Energy for Green Ammonia
-
Research Article
-
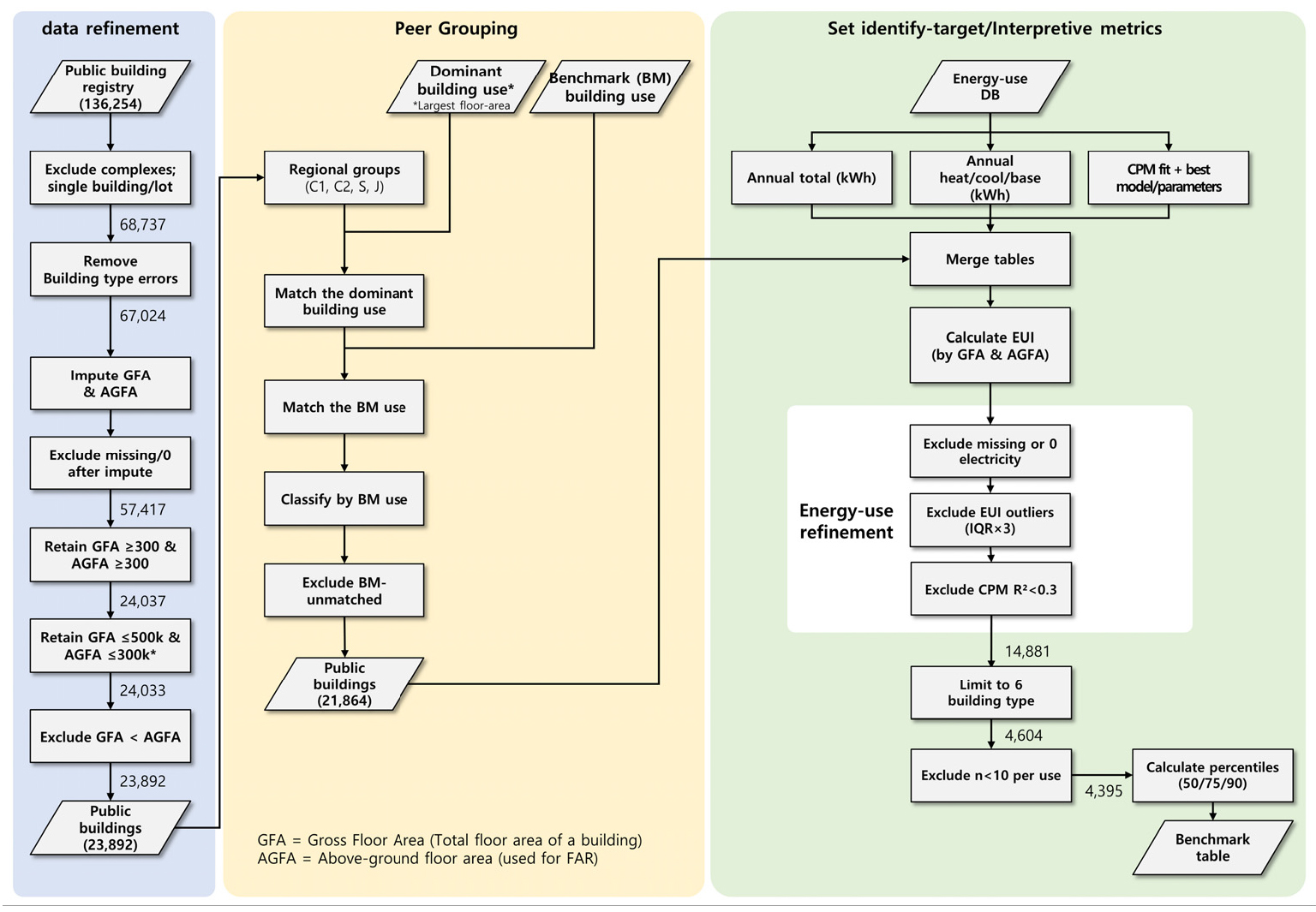
Development of Assessment Indicators for Selecting Public Buildings for Energy Performance Improvement: Derivation of Benchmarks and Explanatory Indicators
공공건축물 에너지 성능개선 대상 선별관리를 위한 지역·용도별 평가지표 기준값 도출
-
Kim, Hye-Gi, Chu, Han-Gyeong, Kim, Deuk-Woo
김혜기, 추한경, 김덕우
-
Development of Assessment Indicators for Selecting Public Buildings for Energy Performance Improvement: Derivation of Benchmarks and Explanatory Indicators
-
Research Article
-
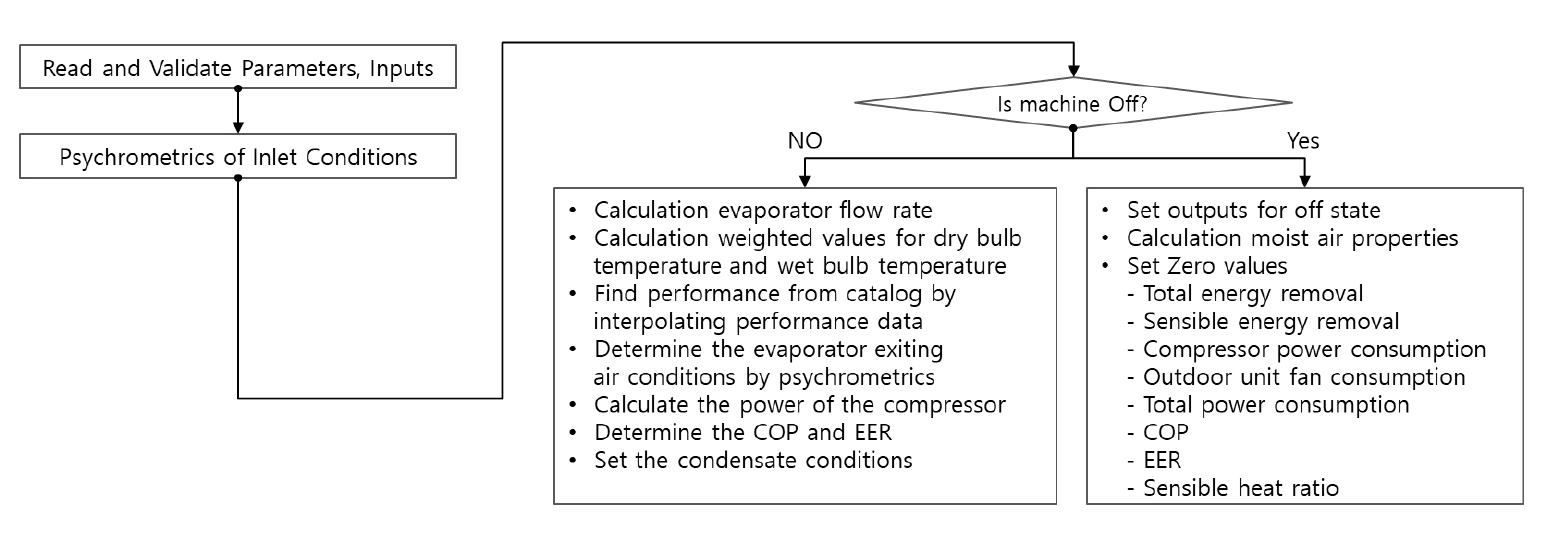
Development of a VRF with Individual Capacity from Combination Ratio Model (VICOR Model) for TRNSYS Application
TRNSYS 적용을 위한 조합비 기반 개별 용량 도출 VRF 모델(VICOR Model) 개발
-
Shin, Dae-Uk, Kim, Min-Hyeong, Kim, Kwang-Woo
신대욱, 김민형, 김광우
-
Development of a VRF with Individual Capacity from Combination Ratio Model (VICOR Model) for TRNSYS Application
-
Research Article
-
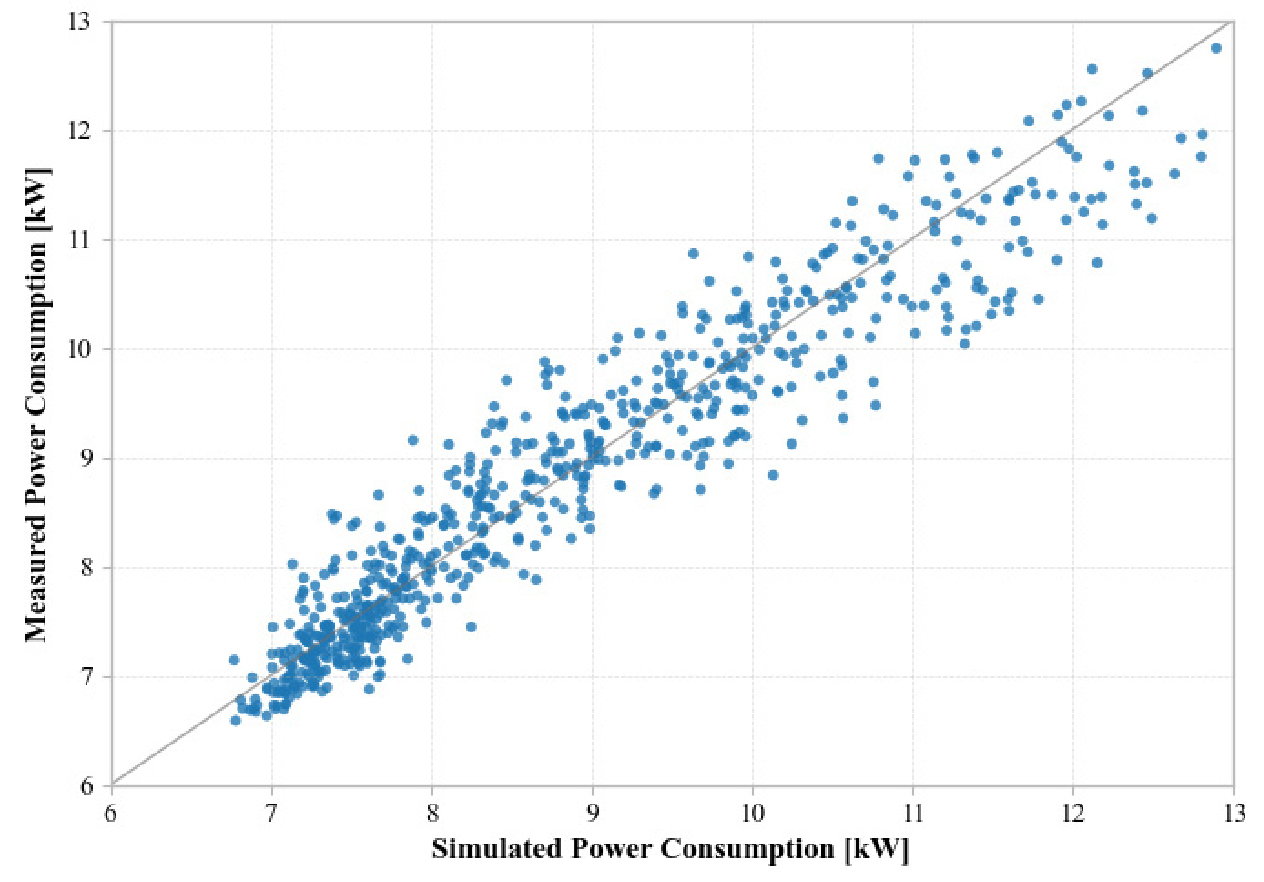
Energy Saving Analysis of Modular Chillers: A Simulation-Based Performance Comparison with a Large Chiller
모듈형 냉동기의 에너지 절감 효과 분석: 시뮬레이션 기반 대형 냉동기 성능 비교 연구
-
Park, Si-Won, Jung, Won-Ho, Kim, Min-Soo, Lee, Je-Hyeon
박시원, 정원호, 김민수, 이제헌
-
Energy Saving Analysis of Modular Chillers: A Simulation-Based Performance Comparison with a Large Chiller
-
Research Article
-
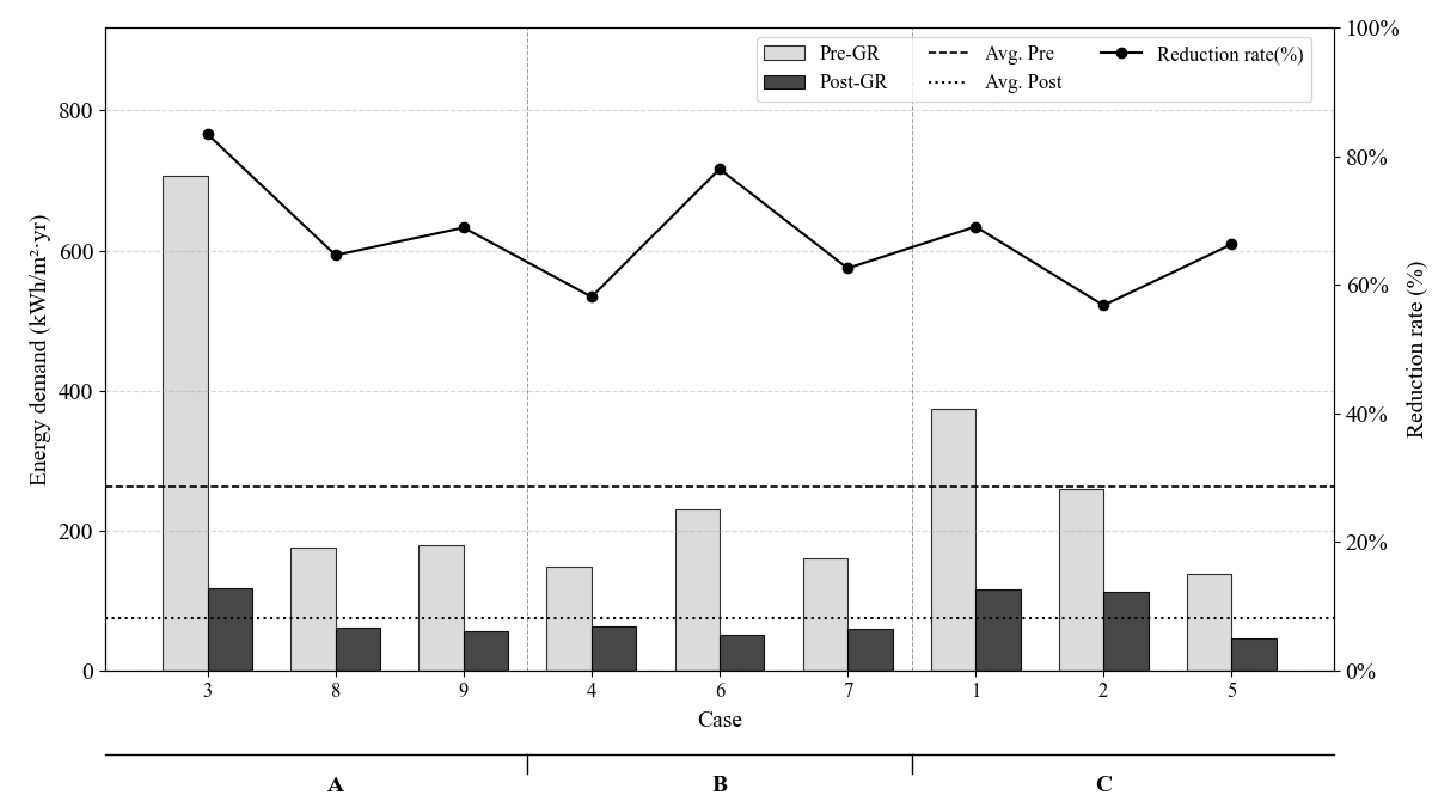
Comparative Analysis of Airtightness and Heating/Cooling Energy Demand Before and After Energy Performance Improvement of Aging Buildings
노후 건축물 에너지 성능 개선 공사 전·후 기밀성능 및 냉난방에너지 요구량 비교 분석
-
Jeon, Ji-Soo, Park, Jong-Il, Choi, Jeong-Man
전지수, 박종일, 최정만
-
Comparative Analysis of Airtightness and Heating/Cooling Energy Demand Before and After Energy Performance Improvement of Aging Buildings
-
Research Article
-
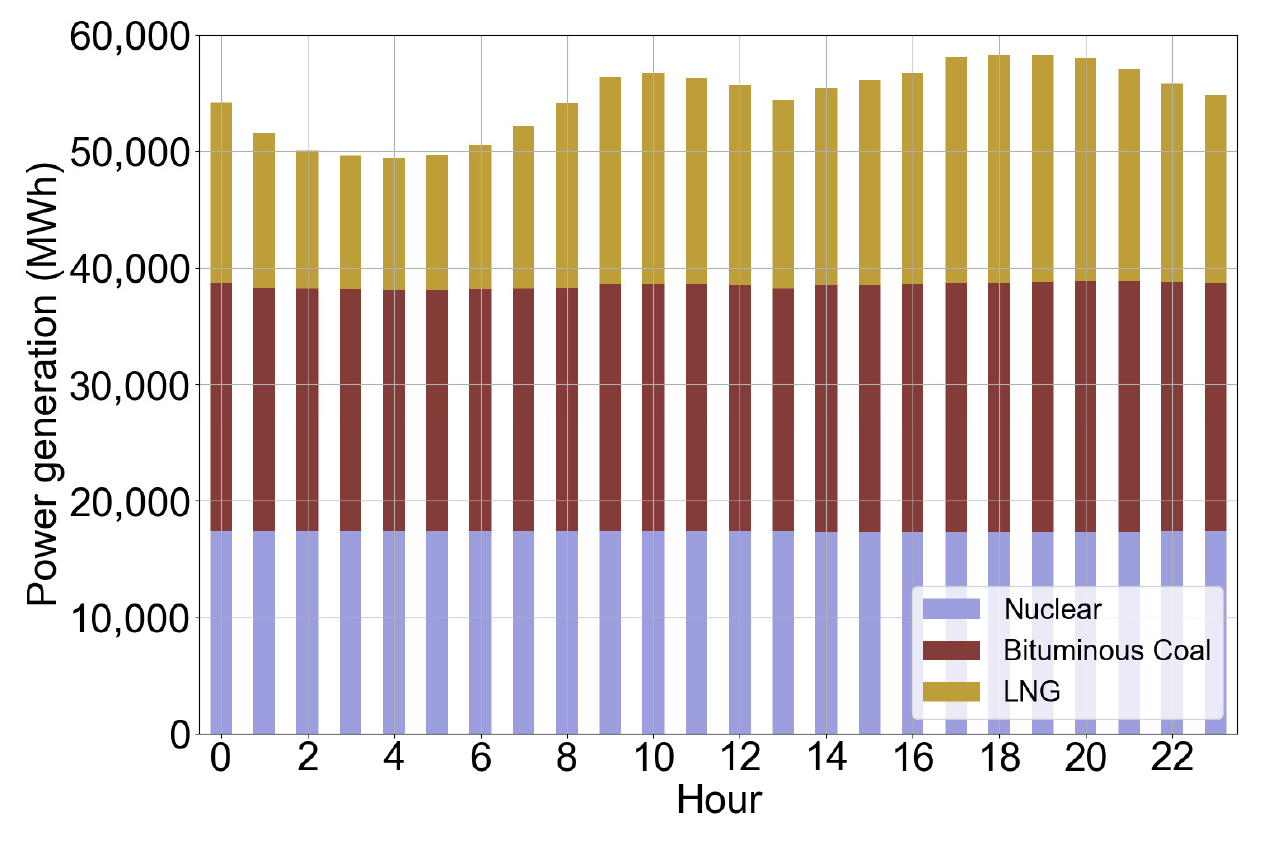
Comparison of Time-Shifting Effects in Building Electricity Use under Separate Environmental and Economic Optimizations
환경성 및 경제성 개별 최적화에 따른 건물 전력사용 시간대 이동 효과 비교
-
Kang, Seong-Yun, Kim, Sun-Sook, Ahn, Hyeunguk
강성윤, 김선숙, 안형욱
-
Comparison of Time-Shifting Effects in Building Electricity Use under Separate Environmental and Economic Optimizations
-
Research Article
-
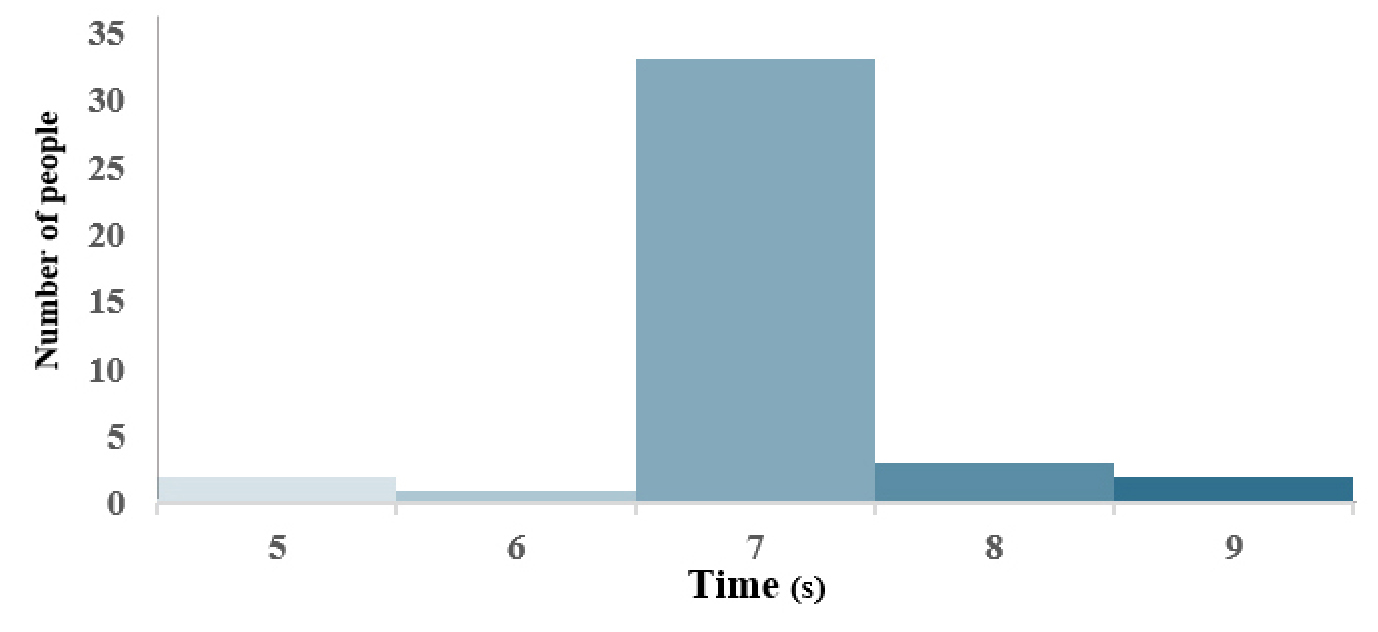
Derivation of The Entrance Correction Factor (Ce) Considering Occupant Traffic rate
이용자 통행량을 고려한 유동보정계수 Ce 도출
-
Park, Soo-Ha, Park, So-Yi, Jing, Jia-Jun, Jo, Jae-Hun
박수하, 박소이, 정가준, 조재훈
-
Derivation of The Entrance Correction Factor (Ce) Considering Occupant Traffic rate
-
Research Article
-
Research Article
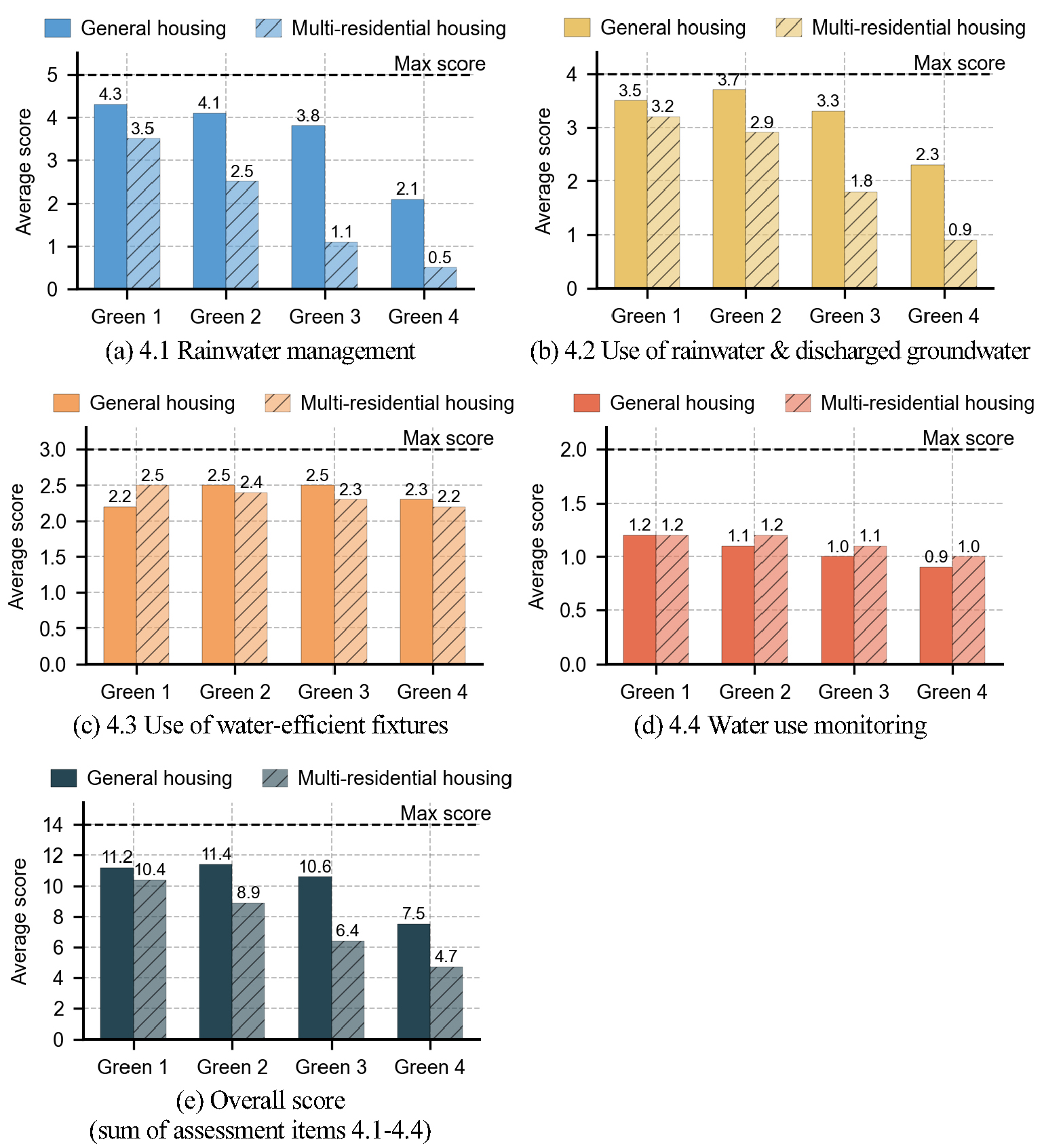
-
An Empirical Analysis of G-SEED Certification Results for Newly Constructed Residential Buildings: A Focus on Water Management
신축 주거용 건축물의 G-SEED 인증 현황 분석: 물순환 관리 분야를 중심으로
-
Yoo, Young-Seo, Cho, Kyung-Joo, Seo, Sung-Mo, Yoon, Yo-Sun, Jang, Dae-Hee
유영서, 조경주, 서성모, 윤요선, 장대희
-
An Empirical Analysis of G-SEED Certification Results for Newly Constructed Residential Buildings: A Focus on Water Management
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of Korean Institute of Architectural Sustainable Environment and Building Systems
Journal of Korean Institute of Architectural Sustainable Environment and Building Systems
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of Korean Institute of Architectural Sustainable Environment and Building Systems
Journal of Korean Institute of Architectural Sustainable Environment and Building Systems











