-
Research Article
-
Comparative Techno-Economic Analysis of Hydrogen Production Process Facility and Renewable Energy for Green Ammonia
그린 암모니아를 위한 수소생산 공정설비와 재생에너지 기술-경제적 비교 분석
-
Kim, Ji-Ho, Yoshioka, Takuyuki, Kim, Jee-Young, Gwon, Min-Ji, Kim, Hyun-Bae
김지호, 요시오카타쿠유키, 김지영, 권민지, 김현배
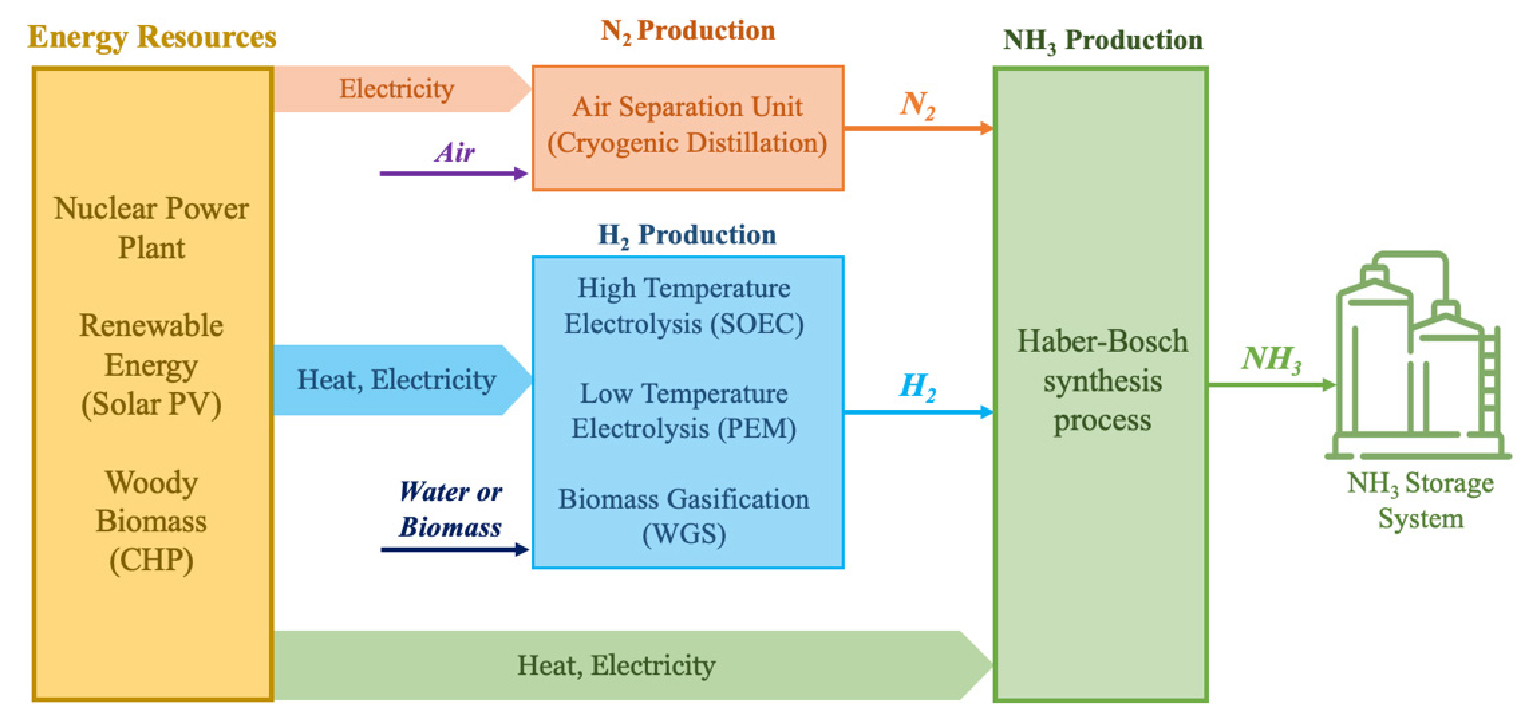
- We evaluate three commercial-scale routes to green ammonia using a process simulator for a 1,000 t·d⁻¹ plant and report the 2023-USD levelized …
- We evaluate three commercial-scale routes to green ammonia using a process simulator for a 1,000 t·d⁻¹ plant and report the 2023-USD levelized cost of ammonia (LCOA). The facility integrates an air separation unit with a Haber–Bosch synthesis loop and is coupled to one of three options. Scenario 1 (S1): nuclear power and solid-oxide electrolysis (SOEC); Scenario 2 (S2): solar photovoltaic (PV) power and proton exchange membrane (PEM) electrolysis; Scenario 3 (S3): biomass combined heat and power (CHP) with gasification and CO2 capture. Equipment sizes are set by mass- and energy-balance calculations. Capital expenditure (CAPEX) and operating expenditure (OPEX) are estimated using standard chemical engineering cost methods with sensitivity analyses. Base-case LCOA (USD·t⁻¹) are S1: 539.73; S2: 646.28; S3: 602.35. Best–worst ranges are S1: 470.23–613.08; S2: 576.39–715.82; S3: 535.79–672.31. S1 is broadly applicable where stable heat and electricity enable strong integration, although the SOEC stack remains a risk. S2 is attractive in regions that can supply large quantities of low-cost renewable electricity to satisfy its extreme power demand. S3 is advantageous in the presence of abundant forest resources and supply networks because of its low power consumption. These results suggest that the green ammonia process is crucial for achieving carbon neutrality through regionally adjusted routes. - COLLAPSE
-
Comparative Techno-Economic Analysis of Hydrogen Production Process Facility and Renewable Energy for Green Ammonia
-
Research Article
-
Development of Assessment Indicators for Selecting Public Buildings for Energy Performance Improvement: Derivation of Benchmarks and Explanatory Indicators
공공건축물 에너지 성능개선 대상 선별관리를 위한 지역·용도별 평가지표 기준값 도출
-
Kim, Hye-Gi, Chu, Han-Gyeong, Kim, Deuk-Woo
김혜기, 추한경, 김덕우
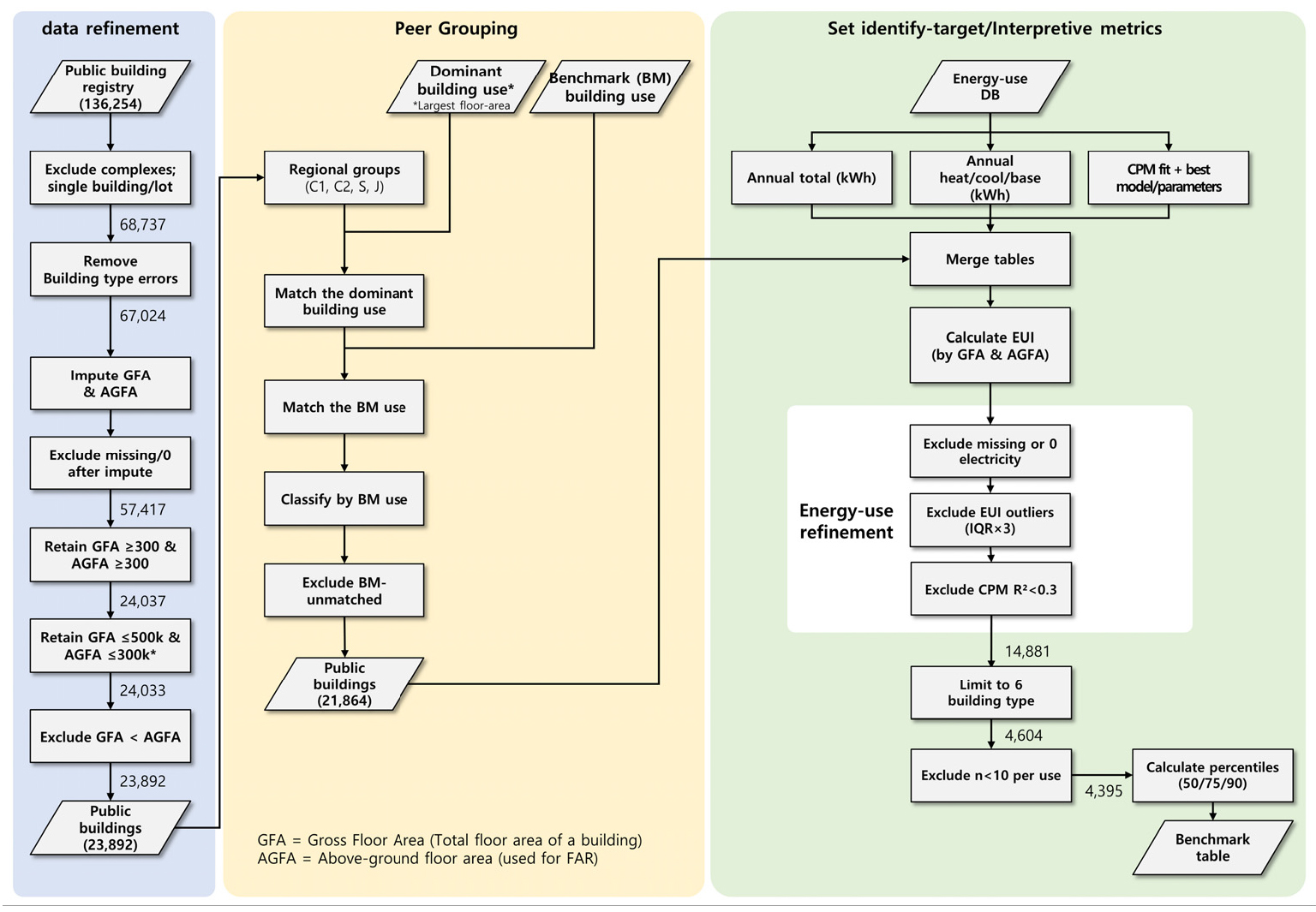
- Current energy evaluation systems for public buildings in Korea rely on simple classification with only 5 climate regions and 6 major building …
- Current energy evaluation systems for public buildings in Korea rely on simple classification with only 5 climate regions and 6 major building uses, lacking the granularity needed to accurately identify buildings requiring performance improvements. Moreover, existing approaches focus solely on total annual energy consumption without considering seasonal variations or providing diagnostic insights into energy performance causes. This study addresses these limitations by developing a comprehensive dual-indicator system comprising screening indicators for target selection and explanatory indicators for performance diagnosis. Using building registry data and monthly energy consumption data from 2018-2019 for 136,256 public buildings, this study established refined classification criteria considering sub-categories within major building uses. A key innovation is the application of calendarization techniques to align billing periods with calendar months, followed by simplified weather-related energy disaggregation to separate heating, cooling, and base loads. Change Point Models were applied to derive explanatory indicators including heating/cooling sensitivities and change-point temperatures, providing insights into building envelope performance and operational characteristics. The final analysis of 4,395 buildings yielded differentiated benchmarks by building use and region, enabling both effective screening of energy-intensive buildings and diagnosis of underlying performance issues. This dual-indicator approach significantly improves upon existing methods by providing actionable insights for targeted energy retrofit strategies. - COLLAPSE
-
Development of Assessment Indicators for Selecting Public Buildings for Energy Performance Improvement: Derivation of Benchmarks and Explanatory Indicators
-
Research Article
-
Development of a VRF with Individual Capacity from Combination Ratio Model (VICOR Model) for TRNSYS Application
TRNSYS 적용을 위한 조합비 기반 개별 용량 도출 VRF 모델(VICOR Model) 개발
-
Shin, Dae-Uk, Kim, Min-Hyeong, Kim, Kwang-Woo
신대욱, 김민형, 김광우
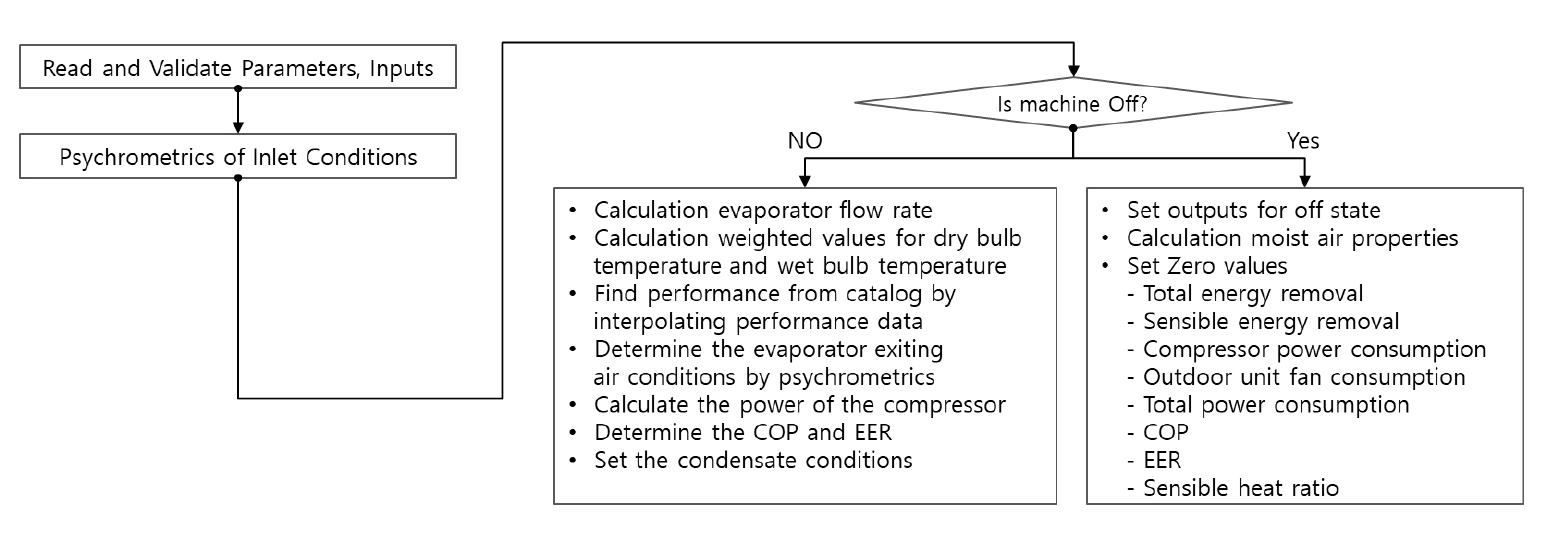
- This study developed VICOR model, a TRNSYS component for Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) systems. It directly inputs up to 100 indoor units, …
- This study developed VICOR model, a TRNSYS component for Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) systems. It directly inputs up to 100 indoor units, automatically calculates real-time combination ratio based on operating units, and performs 5-dimensional interpolation using manufacturer catalog data (indoor/outdoor dry-bulb temperatures, indoor wet-bulb temperature, airflow, and combination ratio). Diverse indoor conditions are integrated via load-weighted averaging, and total cooling capacity is proportionally distributed to each room’s instantaneous load. Validation with a 5-zone cooling simulation showed set-temperature (26°C) satisfaction of 98.0–99.3%, RMSE 0.21–0.49°C, and CVRMSE 2.0–2.3%. - COLLAPSE
-
Development of a VRF with Individual Capacity from Combination Ratio Model (VICOR Model) for TRNSYS Application
-
Research Article
-
Energy Saving Analysis of Modular Chillers: A Simulation-Based Performance Comparison with a Large Chiller
모듈형 냉동기의 에너지 절감 효과 분석: 시뮬레이션 기반 대형 냉동기 성능 비교 연구
-
Park, Si-Won, Jung, Won-Ho, Kim, Min-Soo, Lee, Je-Hyeon
박시원, 정원호, 김민수, 이제헌
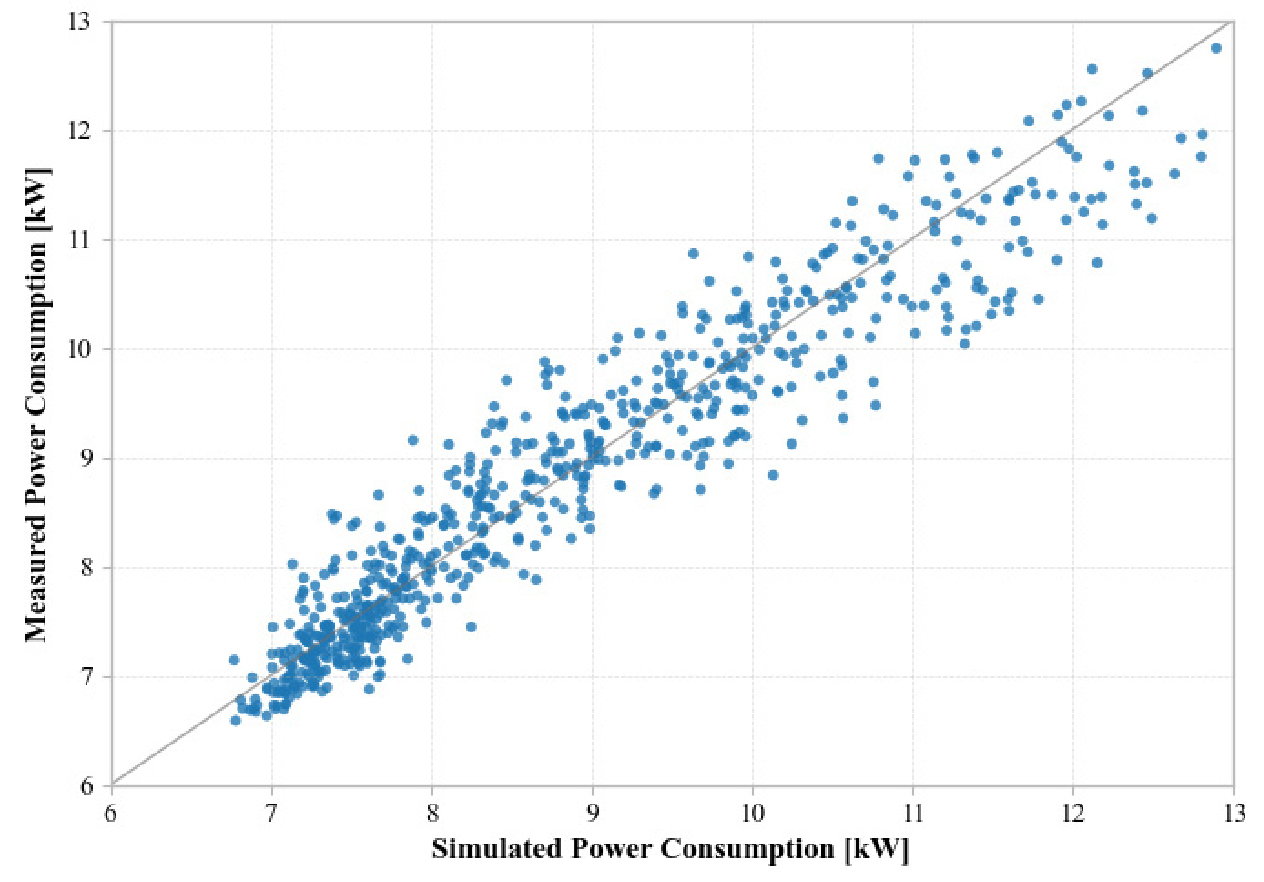
- Cooling electricity demand in office buildings is largely governed by chiller performance under part-load conditions. This study evaluates a modular chiller system …
- Cooling electricity demand in office buildings is largely governed by chiller performance under part-load conditions. This study evaluates a modular chiller system against a single large chiller using an EnergyPlus model of a DOE large office with two air-cooled plants: a constant-speed chiller (993.8 kW) and a modular system of fifteen 65 kW variable-speed units (975 kW). The performance curves of the modular chillers were derived using manufacturer catalog and field measurement data, and the simulation model was calibrated to ensure an accuracy level of CV(RMSE) = 6.5% against measured power consumption. For the cooling season from May to September, with a common cooling load profile and weather file, the modular system operated at part-load ratios of 0.7~0.8 and COPs of 3.6~3.9, while the large chiller operated at 0.25~0.45 and COPs of 2.4~3.0. Total cooling electricity use of the modular system was 104.4 MWh, 24.7% lower than that of the large chiller (138.7 MWh), indicating that modular chillers can substantially reduce cooling electricity use under part-load-dominated conditions in office buildings. - COLLAPSE
-
Energy Saving Analysis of Modular Chillers: A Simulation-Based Performance Comparison with a Large Chiller
-
Research Article
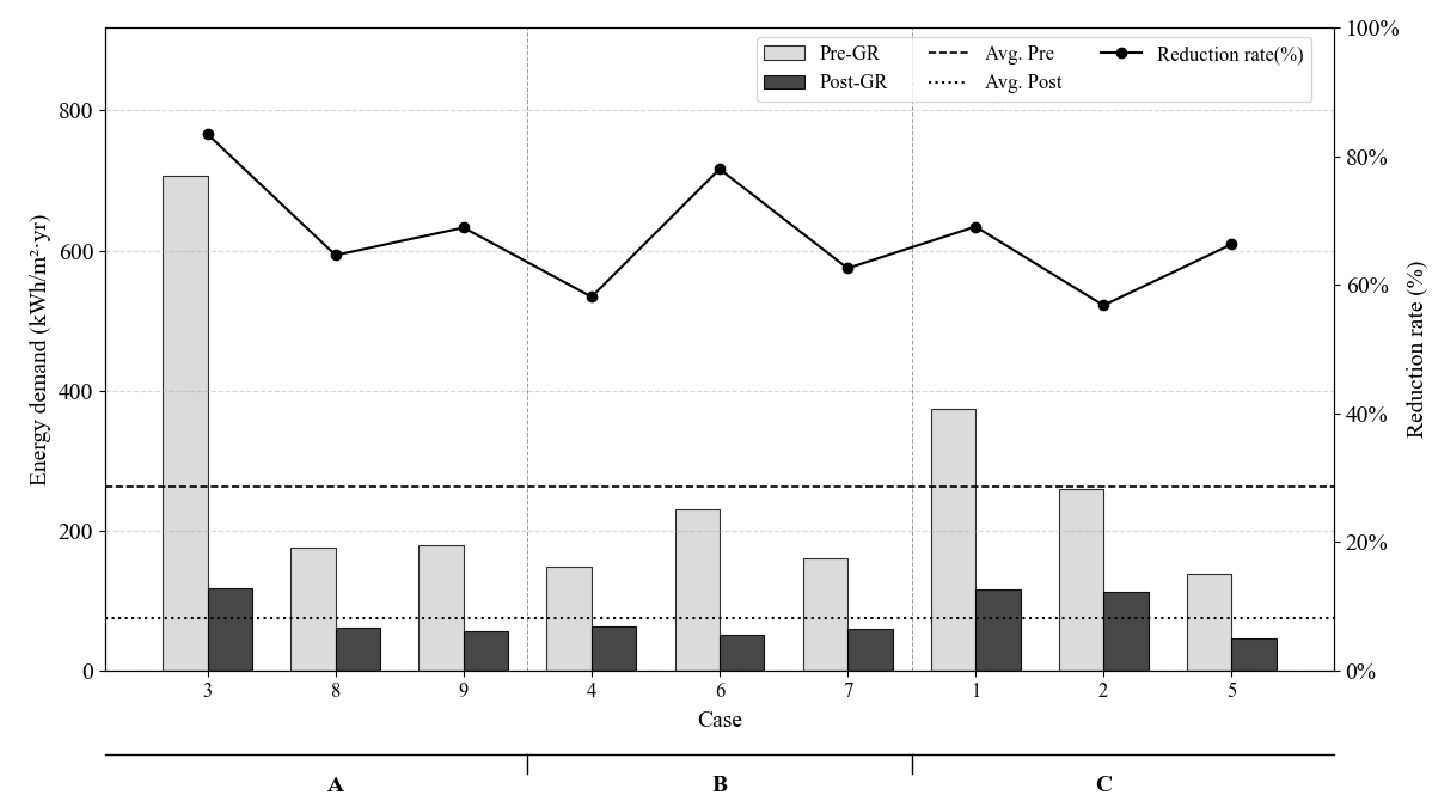
-
Comparative Analysis of Airtightness and Heating/Cooling Energy Demand Before and After Energy Performance Improvement of Aging Buildings
노후 건축물 에너지 성능 개선 공사 전·후 기밀성능 및 냉난방에너지 요구량 비교 분석
-
Jeon, Ji-Soo, Park, Jong-Il, Choi, Jeong-Man
전지수, 박종일, 최정만
- This study empirically analyzes the impact of airtightness on actual energy performance by measuring airtightness and heating and cooling energy demand before …
- This study empirically analyzes the impact of airtightness on actual energy performance by measuring airtightness and heating and cooling energy demand before and after energy performance improvement projects in aging buildings. A total of nine buildings were evaluated using Blower Door Tests based on ISO 9972 and energy simulations based on ISO 13790. The results confirmed statistically significant improvements in both heating and cooling energy demand and airtightness performance following the retrofits. However, an analysis by building scale revealed a distinct limitation: unlike small-scale buildings, large-scale buildings exhibited a markedly lower rate of airtightness improvement. Furthermore, among heat loss factors, infiltration was identified as the variable with the highest fluctuation, indicating that structural complexity in larger buildings poses a significant risk to energy efficiency. These findings imply that conventional approaches, primarily focused on replacing insulation and windows, have limitations in securing adequate airtightness for large-scale buildings due to their complex mechanical penetrations. Consequently, this study suggests the necessity of introducing institutional management standards for airtightness and establishing differentiated construction management guidelines based on building scale to ensure stable energy saving effects in energy retrofit projects. - COLLAPSE
-
Comparative Analysis of Airtightness and Heating/Cooling Energy Demand Before and After Energy Performance Improvement of Aging Buildings
-
Research Article
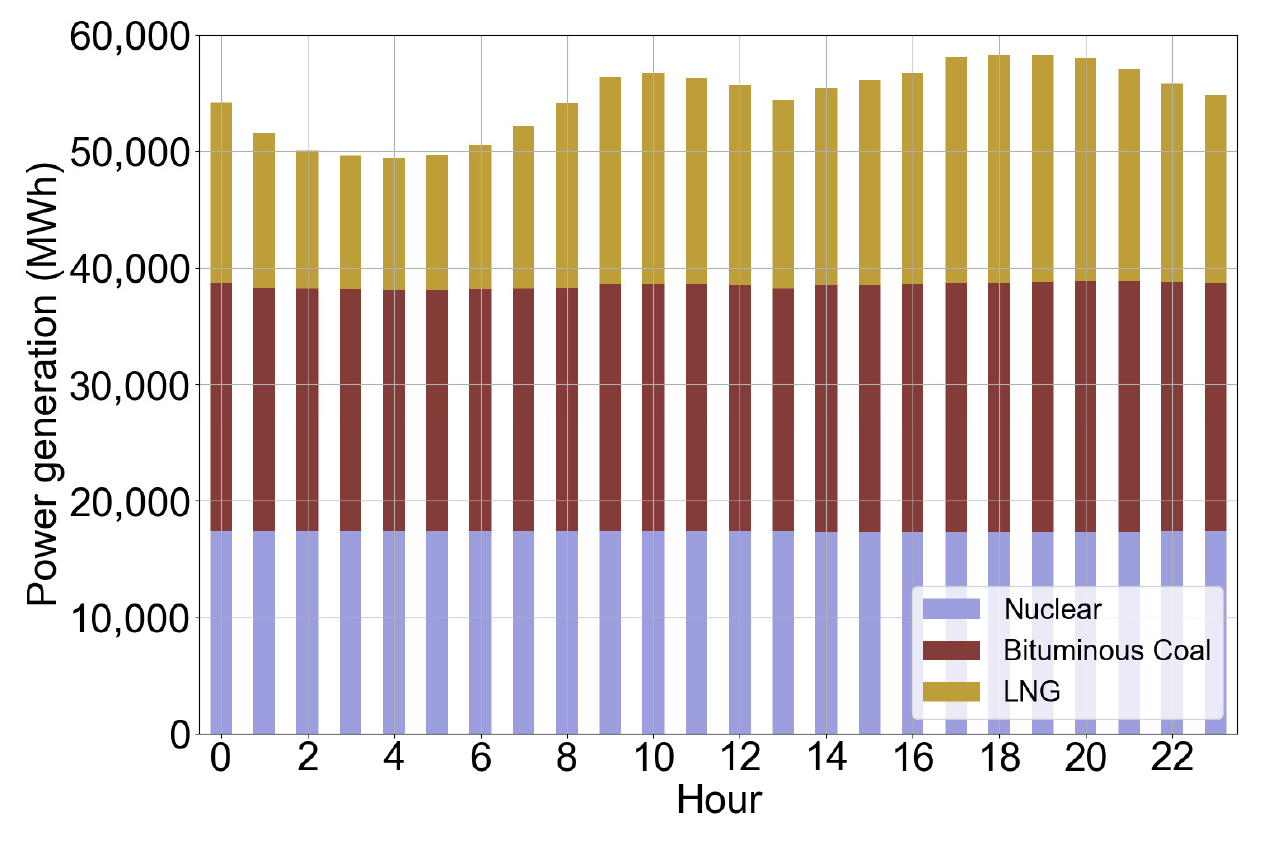
-
Comparison of Time-Shifting Effects in Building Electricity Use under Separate Environmental and Economic Optimizations
환경성 및 경제성 개별 최적화에 따른 건물 전력사용 시간대 이동 효과 비교
-
Kang, Seong-Yun, Kim, Sun-Sook, Ahn, Hyeunguk
강성윤, 김선숙, 안형욱
- This study quantifies how MEF-based and TOU-based operating strategies produce different electricity time-shifting outcomes in a Korean factory building. Using Korean public …
- This study quantifies how MEF-based and TOU-based operating strategies produce different electricity time-shifting outcomes in a Korean factory building. Using Korean public data for 2020, we estimated seasonal hourly marginal emission factors (MEFs) by identifying fuel sources that respond to demand-driven generation changes and regressing hourly changes in CO2 emissions on changes in generation. The resulting MEFs were linked to hourly EMS electricity use of one manufacturing facility and to the 2020 seasonal time-of-use (TOU) tariff. We then performed daily nonlinear time-shifting optimization of hourly electricity use across the full year under conservative constraints—daily energy conservation, adjustment bounds, and ramp-rate similarity—to evaluate time-shifting effects without reducing total electricity use. Estimated MEFs ranged from 0.17 to 0.73 kgCO2/kWh (a 4.3-fold difference), indicating that identical electricity use can yield substantially different emissions depending on timing. Under the MEF objective, annual emissions decreased by 4.91 tCO2 with an additional cost of approximately 0.70 million KRW. Under the TOU objective, the annual bill decreased by about 2.76 million KRW while emissions increased by 1.30 tCO2. Because the constraints intentionally limit operational flexibility, these impacts should be interpreted as conservative estimates of time-shifting benefits and penalties. Overall, the results reveal a clear emissions–cost trade-off and support the need for multi-objective or weighted decision frameworks that jointly consider MEF and TOU in building-level operation. - COLLAPSE
-
Comparison of Time-Shifting Effects in Building Electricity Use under Separate Environmental and Economic Optimizations
-
Research Article
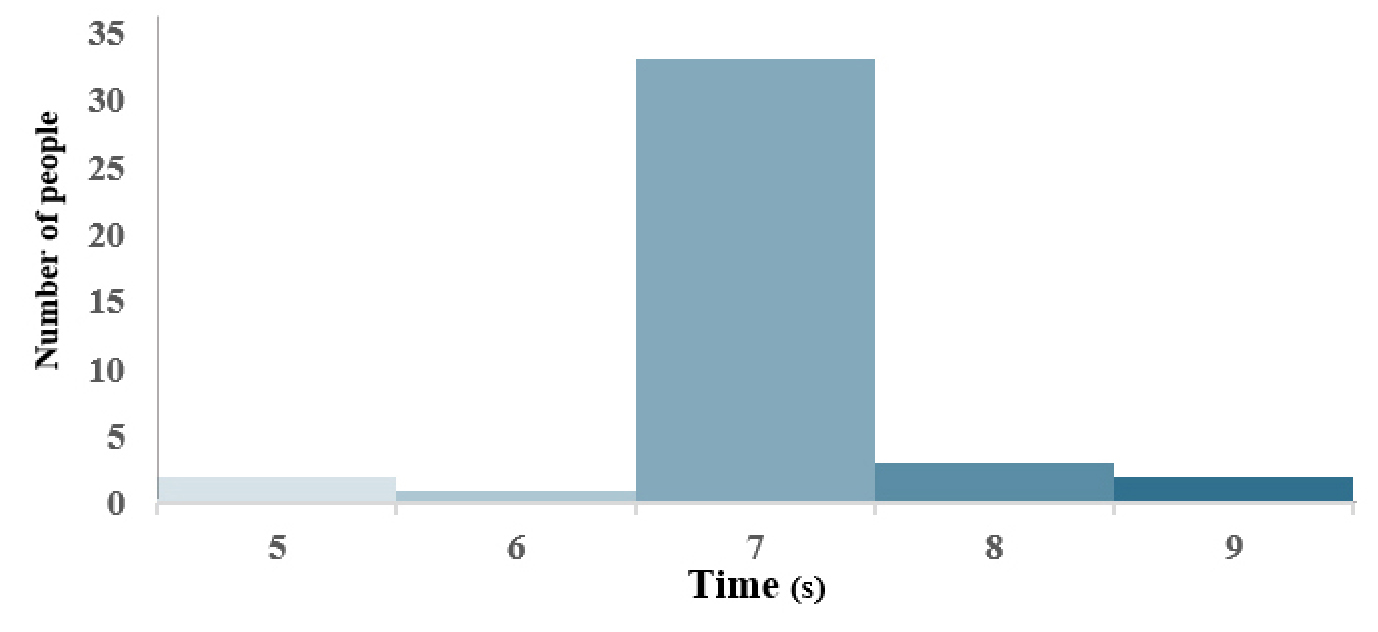
-
Derivation of The Entrance Correction Factor (Ce) Considering Occupant Traffic rate
이용자 통행량을 고려한 유동보정계수 Ce 도출
-
Park, Soo-Ha, Park, So-Yi, Jing, Jia-Jun, Jo, Jae-Hun
박수하, 박소이, 정가준, 조재훈
- This study aims to develop a realistic infiltration calculation method for building entrance doors by simultaneously considering pressure difference and occupant traffic. …
- This study aims to develop a realistic infiltration calculation method for building entrance doors by simultaneously considering pressure difference and occupant traffic. Door infiltration was divided into two components: leakage infiltration when the door is closed and airflow through the opening during door operation. Leakage infiltration was modeled using a power-law relationship, while infiltration during door opening was evaluated by introducing an entrance correction factor ( C e ) into the conventional large opening formulation to reflect the dynamic characteristics of door movement. To derive the entrance correction factor, controlled laboratory experiments were conducted under various pressure differences, traffic scenarios, and vestibule conditions. Preliminary experiments were performed to determine representative door opening duration and maximum opening angle based on actual occupant behavior. Door infiltration rates were then measured for multiple opening scenarios representing intermittent opening, continuous reopening, and sustained opening conditions. The experiments were repeated across a range of pressure differences to quantify their combined effects. The results indicate that door infiltration increases with both pressure difference and occupant traffic, with sustained opening conditions producing the highest infiltration rates. The presence of a vestibule significantly reduced infiltration, particularly under high-traffic conditions. Based on the experimental data, entrance correction factors were derived and expressed as regression functions of occupant traffic. The proposed method enables the dynamic effects of door operation to be incorporated into infiltration calculations, addressing limitations of existing static approaches. By introducing an entrance correction factor that reflects realistic door usage patterns, this study provides a practical framework for improving the accuracy of entrance door infiltration estimation and enhancing the reliability of building energy analysis. - COLLAPSE
-
Derivation of The Entrance Correction Factor (Ce) Considering Occupant Traffic rate
-
Research Article
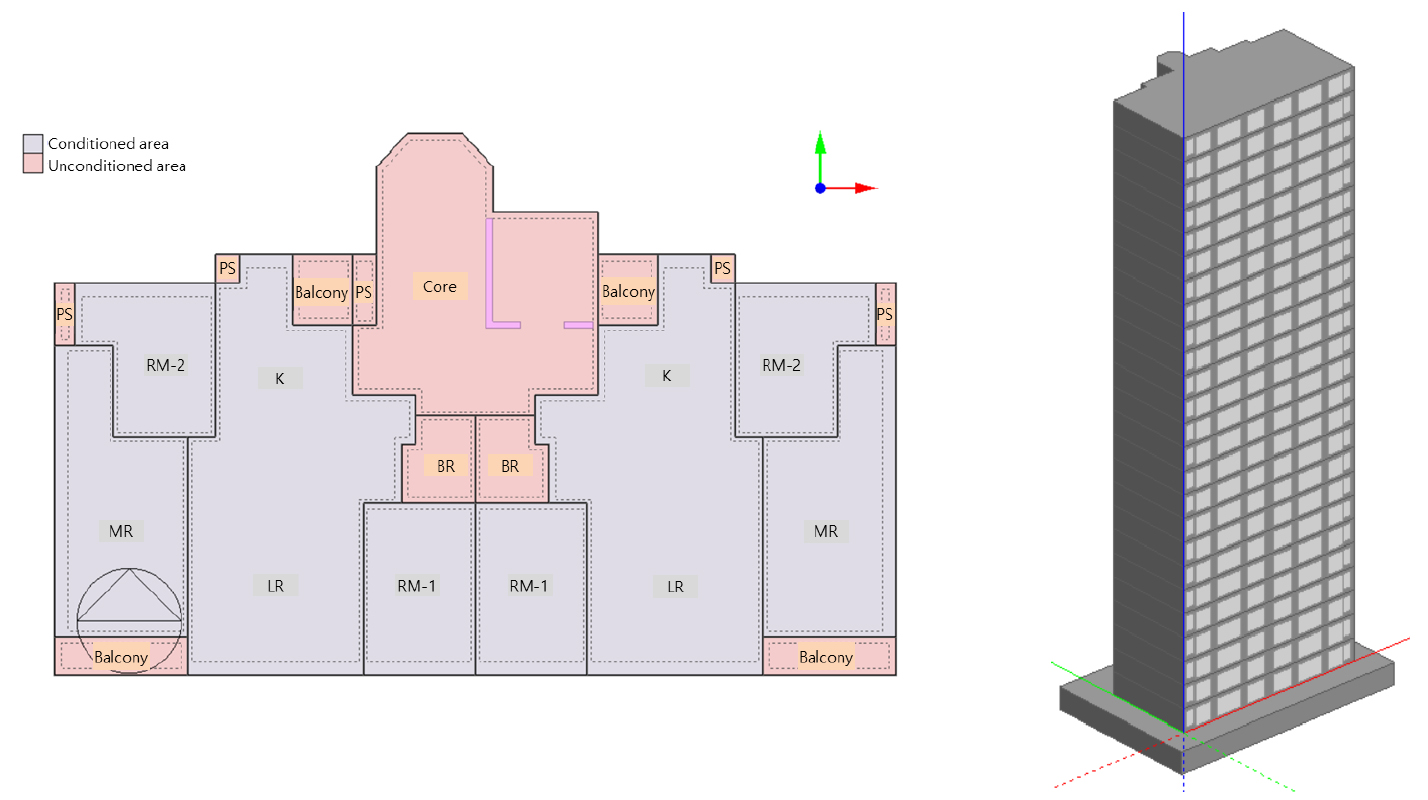
-
A Preliminary Study on Heating Load Savings through Enhanced Insulation in Unheated North-Facing Common Spaces of Apartments
아파트 북측 비난방 공용공간의 단열 보강과 난방부하 절감 효과에 대한 기초 연구
-
Chang, Hyun-Jae
장현재
- In Seoul, South Korea (37.6°N), north-facing building envelopes receive no direct solar radiation during winter and are exposed only to diffuse solar …
- In Seoul, South Korea (37.6°N), north-facing building envelopes receive no direct solar radiation during winter and are exposed only to diffuse solar radiation. In typical Korean apartment buildings, which predominantly adopt reinforced concrete wall-bearing systems, heat transfer through north-side concrete walls is expected to be affected not only by indoor–outdoor temperature differences but also by the substantial thermal mass of concrete. This study investigated the winter heat transfer behavior of unheated north-facing common spaces in a flat-type apartment building, focusing on heat flux and surface temperature responses of envelope components. The influence of concrete thermal capacity was examined, and the potential heating load reduction achieved through insulation reinforcement was evaluated. The results showed that the external wall accounted for the largest heat loss among the components of the common space. Heat flux through the external wall exhibited a time lag of approximately 4 h in response to outdoor temperature variations. In the common space wall, heat loss occurred at the inner surface while heat gain was observed at the outer surface during periods when outdoor air temperature exceeded the core air temperature. This indicates that heat transfer was governed not only by instantaneous temperature differences but also by time-delay and attenuation effects of temperature variation associated with concrete thermal mass. Insulation reinforcement of 30 mm applied to the core wall reduced the heating load by 2.4%. Extending the insulation to the kitchen-side balcony increased the reduction to 3.9%, while including the north-facing pipe shaft further enhanced the predicted reduction to 6.1%. - COLLAPSE
-
A Preliminary Study on Heating Load Savings through Enhanced Insulation in Unheated North-Facing Common Spaces of Apartments
-
Research Article
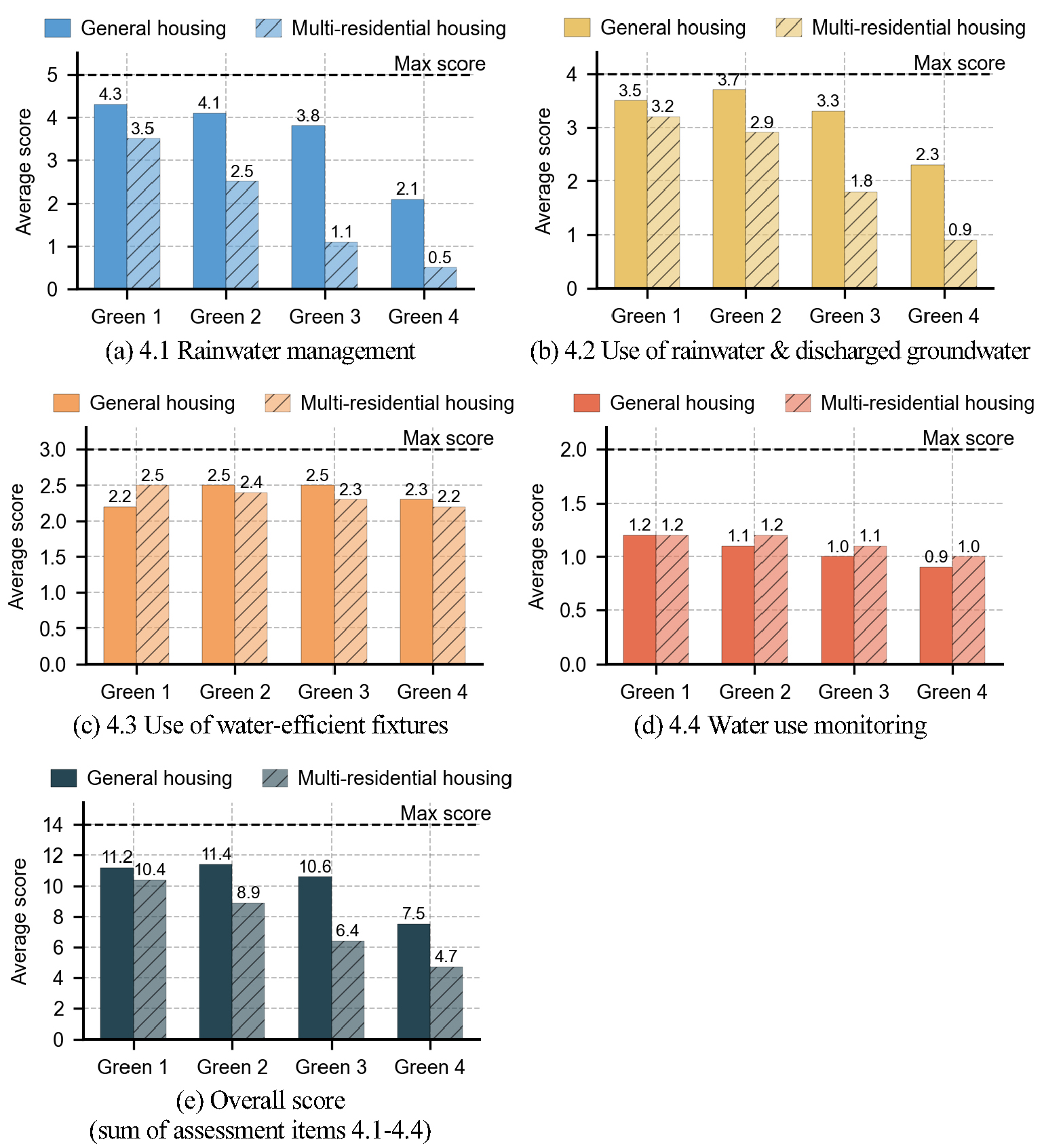
-
An Empirical Analysis of G-SEED Certification Results for Newly Constructed Residential Buildings: A Focus on Water Management
신축 주거용 건축물의 G-SEED 인증 현황 분석: 물순환 관리 분야를 중심으로
-
Yoo, Young-Seo, Cho, Kyung-Joo, Seo, Sung-Mo, Yoon, Yo-Sun, Jang, Dae-Hee
유영서, 조경주, 서성모, 윤요선, 장대희
- The Green Standard for Energy and Environmental Design (G-SEED) provides a comprehensive framework for evaluating the environmental performance of buildings in South …
- The Green Standard for Energy and Environmental Design (G-SEED) provides a comprehensive framework for evaluating the environmental performance of buildings in South Korea. This study empirically examines how Category 4 (Water Management), which addresses water-use efficiency and water cycle management, is implemented in practice. Certification data from 3,018 newly constructed residential buildings that obtained preliminary G-SEED certification between 2017 and 2024 were analyzed by comparing average scores, normalized achievement ratios, and the distribution of weighting levels across certification grades and residential types. The results indicate that score variations are primarily driven by evaluation items dependent on site conditions and planning strategies,which show pronounced declines in achievement at lower certification grades and frequent zero-score cases. In contrast, equipment- and operation- based items exhibit relatively stable achievement levels across G-SEED grades, functioning largely as baseline requirements. These findings reveal structural differences among evaluation items and suggest potential limitations in the current grading structure in representing continuous performance levels, providing empirical evidence to support further discussion on refining the G-SEED water management evaluation framework. - COLLAPSE
-
An Empirical Analysis of G-SEED Certification Results for Newly Constructed Residential Buildings: A Focus on Water Management
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of Korean Institute of Architectural Sustainable Environment and Building Systems
Journal of Korean Institute of Architectural Sustainable Environment and Building Systems
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of Korean Institute of Architectural Sustainable Environment and Building Systems
Journal of Korean Institute of Architectural Sustainable Environment and Building Systems











