-
Research Article
-
A Study on Development of an Information System for Green Remodeling Data Sharing and Energy Consumption Analysis
그린리모델링 건축물 정보 공유 및 에너지 소요량 분석 지원을 위한 정보 체계 구축 방안 연구
-
Seo, Min-Jeong, Park, Chang-Young, Yang, Chang-Yoon, Jung, Bo-Kyung, Kwon, Young-Cheol, Choi, Chang-Ho
서민정, 박창영, 양창윤, 정보경, 권영철, 최창호
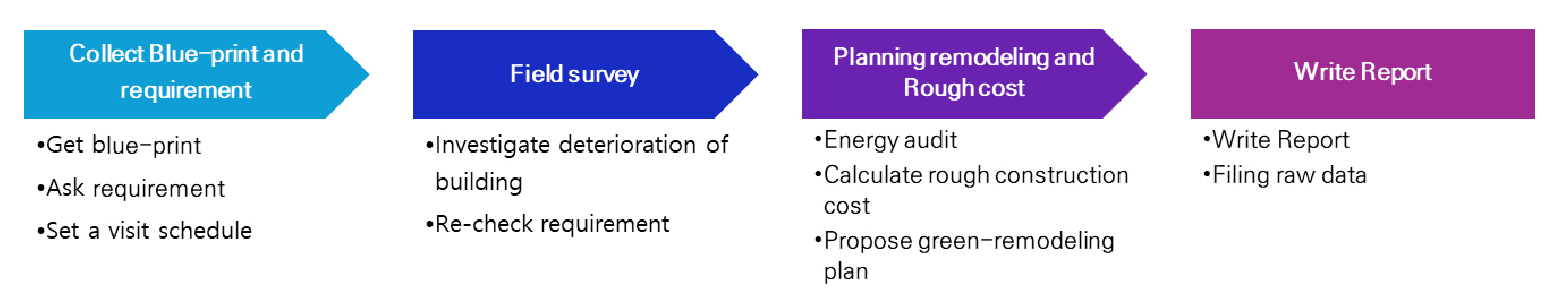
- The purpose of this study is to propose a system that generates information about existing buildings in the planning stage of green …
- The purpose of this study is to propose a system that generates information about existing buildings in the planning stage of green remodeling. The structure of the information generation system was designed based on the input variables of ECO2-OD. As a result of the energy consumption evaluation for two green remodeling demonstration projects, the significance of the developed system was confirmed with an error rate of 9.5 ~ 17.67%. - COLLAPSE
-
A Study on Development of an Information System for Green Remodeling Data Sharing and Energy Consumption Analysis
-
Research Article
-
Hamiltonian Monte Carlo-Based Automated Fault Detection, Diagnosis, and Correction of Outlet Water Temperature Sensor in Heat Pump System
Hamiltonian Monte Carlo 기반 히트펌프 출수온도 센서 자동 고장 감지 진단 및 보정
-
Hong, Seok-Jin, Kim, Hyo-Jun, Lee, Jin-Hyun, Cho, Young-Hum
홍석진, 김효준, 이진현, 조영흠
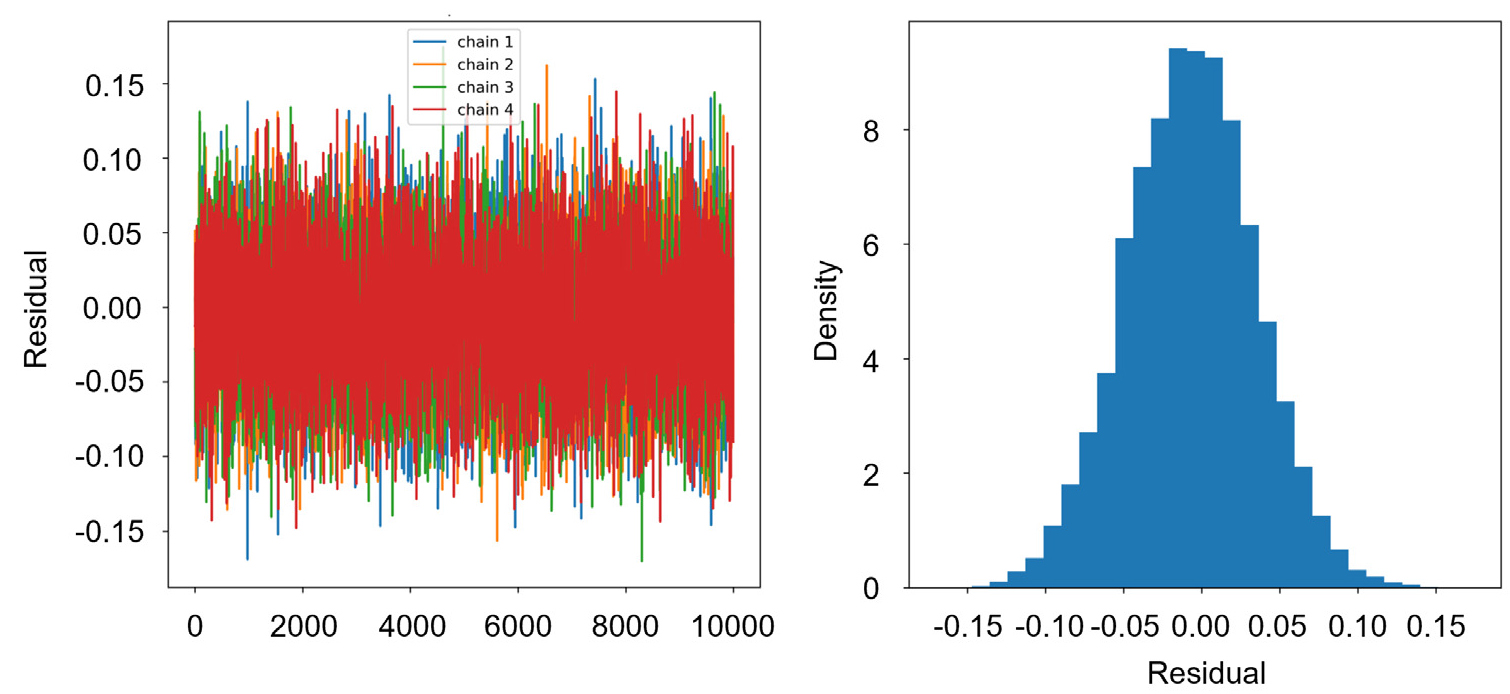
- This study proposes a model based on the Hamiltonian Monte Carlo (HMC) method to automatically detect, diagnose, and correct various errors that …
- This study proposes a model based on the Hamiltonian Monte Carlo (HMC) method to automatically detect, diagnose, and correct various errors that may occur in the outlet water temperature sensor of a heat pump system. To identify factors influencing the formation of the outlet water temperature, experimental data were collected through the Building Automation System (BAS), and the most influential variables were selected using Standardized Regression Coefficient (SRC) analysis. Based on these variables, a heat balance equation was formulated and integrated into the HMC model. Modeling results for steady-state data showed that the proposed model satisfied the ASHRAE Guideline 14 criteria, with a Normalized Mean Bias Error (NMBE) of –0.45% and a Coefficient of Variation of the Root Mean Square Error (CvRMSE) of 0.67%. The coefficient of determination (R²) was 0.9987, confirming a high level of agreement between the measurement and prediction. For performance verification, random errors ranging from –3 to +3℃ in 1℃ increments were introduced, and the posterior distribution were found to closely match the specified errors. In addition, when offset error, random noise error, and drift error were applied to actual operating data, the improvement rates were 84.95%, 81.87%, and 85.67%, respectively. - COLLAPSE
-
Hamiltonian Monte Carlo-Based Automated Fault Detection, Diagnosis, and Correction of Outlet Water Temperature Sensor in Heat Pump System
-
Research Article
-
Improving the Monthly Energy Demand Algorithm Using ISO 13786 Effective Thermal Capacity
ISO 13786 기반 축열 특성 고려를 통한 냉난방 에너지요구량 월간법 알고리즘 보완 연구
-
Lim, Su-Hyun
임수현
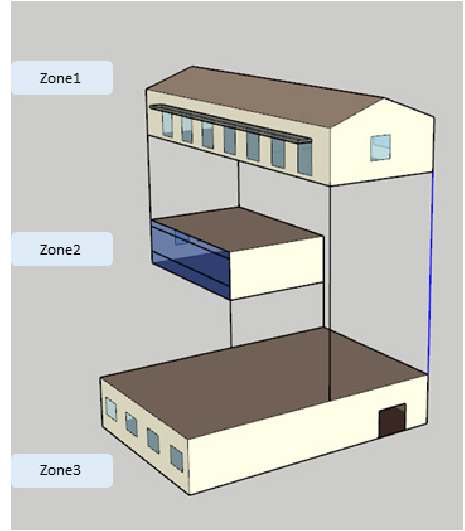
- This study proposes a supplementary algorithm for estimating the effective thermal capacity of building zones based on ISO 13786. Representative material combinations …
- This study proposes a supplementary algorithm for estimating the effective thermal capacity of building zones based on ISO 13786. Representative material combinations were derived for major building elements such as external walls, ceilings, interior walls, and floor slabs using literature data and field surveys. These were statistically validated and reformulated as effective heat capacity per unit floor area, which can be applied in monthly energy demand calculations. A case study demonstrated that the proposed approach more accurately reflects thermal capacity characteristic compared to the simplified classification of ISO 52016-1, while maintaining practical applicability. The results indicate that the method can enhance the accuracy of monthly heating and cooling demand estimation and contribute to the reliability of building energy performance assessments. - COLLAPSE
-
Improving the Monthly Energy Demand Algorithm Using ISO 13786 Effective Thermal Capacity
-
Research Article

-
Analysis of Airtightness Performance and Improvement Strategies for Conventional Buildings in Korea
국내 일반건축물의 기밀성능 현황 분석 및 개선방안 연구
-
Park, Jun-Sung, Lee, Jeong-Hun
박준성, 이정훈
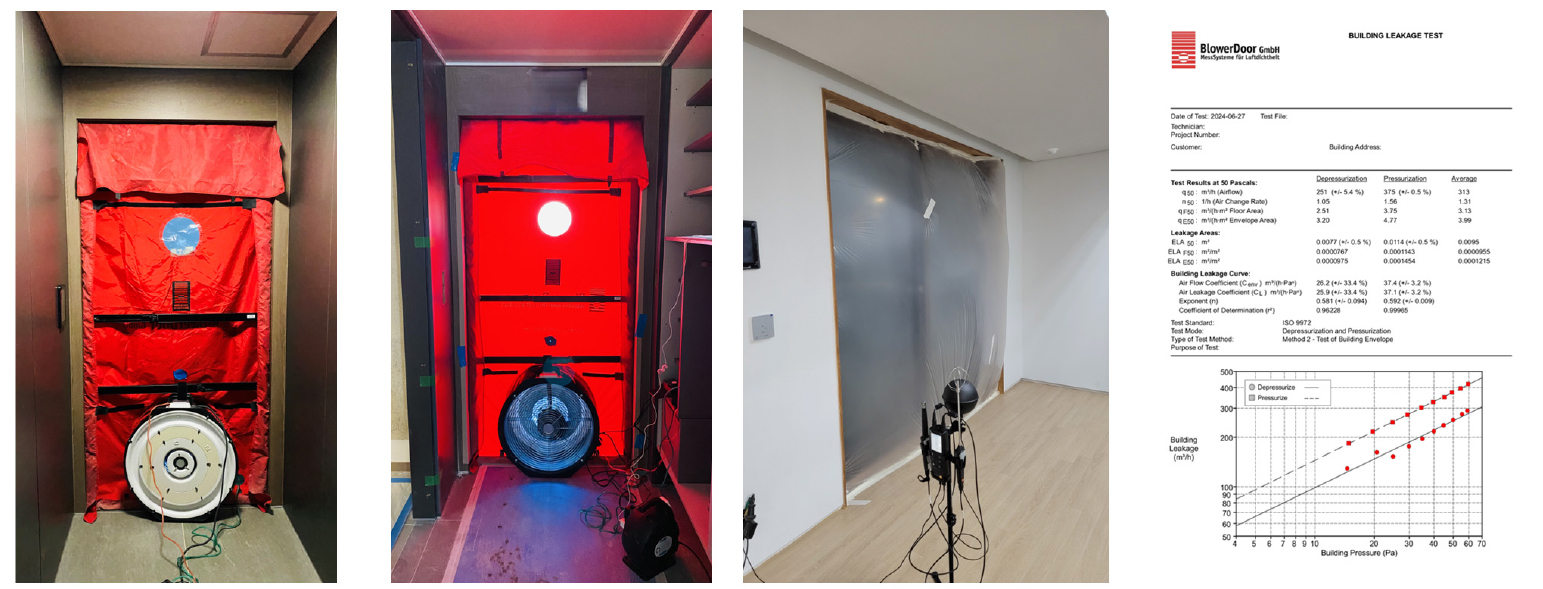
- This study analyzed the current airtightness performance of conventional buildings in Korea and proposed improvement strategies focusing on major leakage points, particularly …
- This study analyzed the current airtightness performance of conventional buildings in Korea and proposed improvement strategies focusing on major leakage points, particularly external service penetrations. Airtightness was measured in approximately 280 buildings of various types and completion years using the Blower Door Test method in accordance with ISO 9972. The buildings were classified as low-energy or conventional depending on whether airtight design and construction elements—such as sealing tapes, membranes, and gaskets—were applied. The analysis revealed that the airtightness performance of conventional buildings varied widely, ranging from 0.56 h-1 to 24.81 h-1. Although more recently constructed buildings tended to exhibit slightly improved airtightness, a significant performance gap remained when compared with low-energy buildings. Field inspections identified the primary leakage sources as external penetrations—including plumbing and electrical service openings in ceilings and walls—where inadequate sealing and incomplete finishing allowed outdoor air to infiltrate. To address these issues, detailed airtight construction methods were proposed, emphasizing the use of soft foam filling, high-performance sealing tapes, and specialized gaskets to ensure continuous airtight layers around service penetrations. These measures are expected to significantly reduce infiltration through building envelopes and improve the overall energy efficiency of existing conventional buildings. This study provides a quantitative overview of airtightness performance in Korean buildings and highlights practical construction details for improving weak points in existing structures, thereby contributing to the advancement of energy-efficient and carbon- neutral building practices. - COLLAPSE
-
Analysis of Airtightness Performance and Improvement Strategies for Conventional Buildings in Korea
-
Research Article
-
A Study on Carbon Emission Feasibility Analysis of Photovoltaic System Application for ZEB Conversion of Passive Buildings Based on LCA
LCA 기반 패시브 건축물의 ZEB 전환을 위한 태양광 설비 적용의 탄소배출 타당성 분석에 관한 연구
-
Kang, Chan-Hyeok, Jung, Bo-Kyung, Kwon, Young-Cheol
강찬혁, 정보경, 권영철
- This study evaluates the carbon-emission feasibility of applying photovoltaic (PV) systems in the process of converting passive buildings into Zero Energy Buildings …
- This study evaluates the carbon-emission feasibility of applying photovoltaic (PV) systems in the process of converting passive buildings into Zero Energy Buildings (ZEB) using a Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) approach. While previous ZEB-related studies have primarily focused on reducing operational energy consumption through the adoption of renewable energy systems, they have often overlooked the embodied carbon emissions generated during the production, transportation, installation, and disposal of such systems. To address this limitation, this study quantitatively compares the life cycle embodied carbon of PV systems with the operational carbon reduction they achieve during use. The embodied carbon emissions were calculated using Environmental Product Declaration (EPD) data and LCA-based emission factors, whereas the operational carbon reduction was estimated by applying regional photovoltaic generation potential and national grid emission factors. The results show that although PV systems generally contribute to enhancing energy self-sufficiency in passive buildings, their net carbon reduction performance varies depending on factors such as installation capacity, regional solar irradiance, and electricity grid intensity. However, in the case examined, the carbon recovery ratio (CRR) exceeded 1, indicating that PV installation achieves a net reduction in life cycle carbon emissions. These findings highlight the necessity of incorporating a carbon-based evaluation framework that considers both embodied and operational emissions when establishing PV application strategies for ZEB implementation. - COLLAPSE
-
A Study on Carbon Emission Feasibility Analysis of Photovoltaic System Application for ZEB Conversion of Passive Buildings Based on LCA
-
Research Article
-
Analysis of Energy Usage Influencing Factors by Type of Medical Facility Using Public Data
공공데이터를 활용한 의료시설 유형별 에너지 사용 영향 인자 분석
-
Kang, Seong-Yun, Kim, Sun-Sook, Ahn, Hyeunguk
강성윤, 김선숙, 안형욱
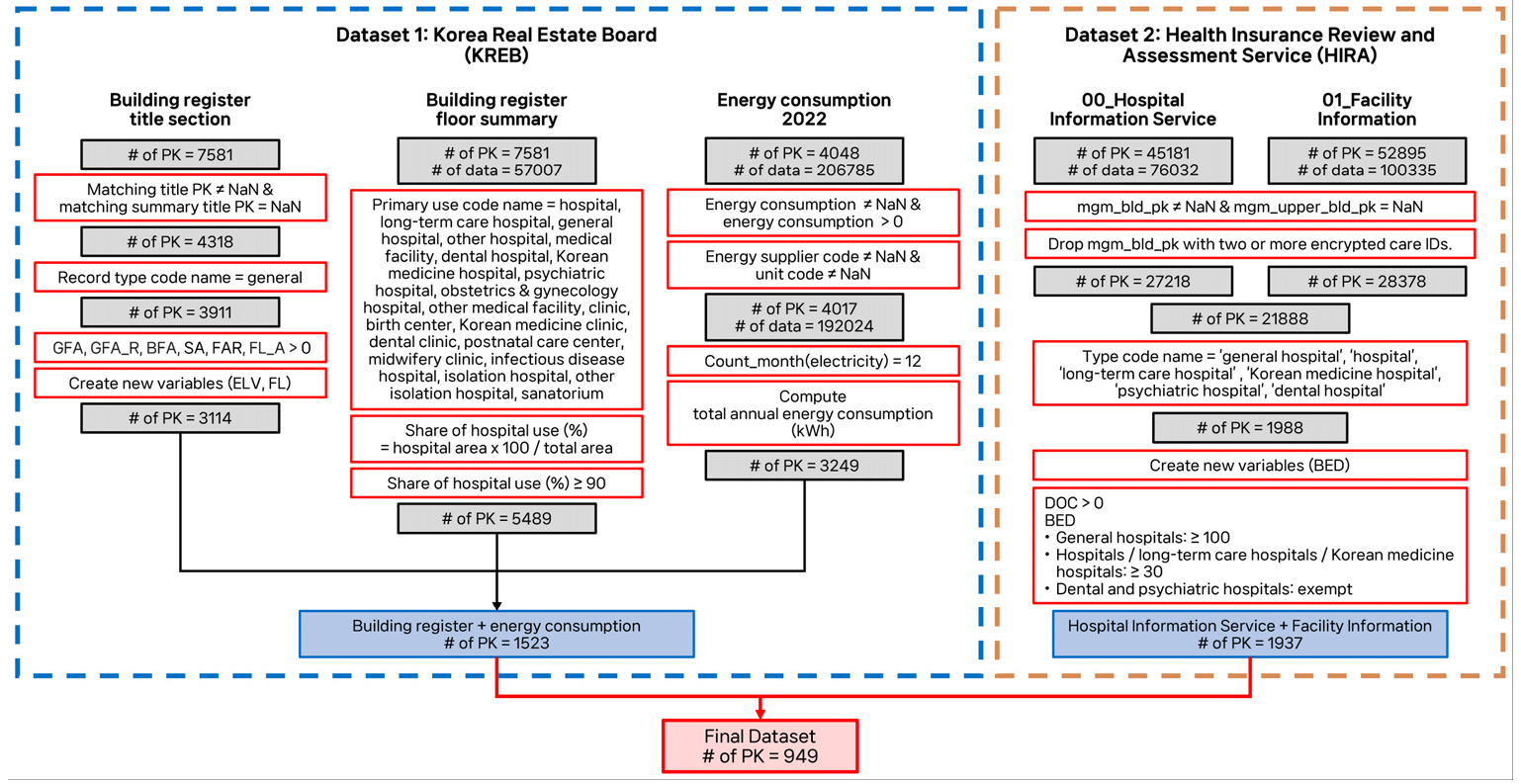
- This study investigates key drivers of energy use in Korean hospital-grade medical facilities using public datasets. After preprocessing data from 932 facilities, …
- This study investigates key drivers of energy use in Korean hospital-grade medical facilities using public datasets. After preprocessing data from 932 facilities, type-specific multiple regression models were developed with stepwise selection. Annual total energy use served as the dependent variable, while gross floor area (GFA), number of doctors (DOC), elevators (ELV), floors (FL), and beds (BED) were candidate predictors. GFA and DOC consistently emerged as major determinants, with ELV influencing general hospitals, and FL and BED affecting long-term care hospitals. Adjusted R² values ranged from 0.92 (general hospitals) to 0.41 (psychiatric hospitals). The negative ELV coefficient likely reflects multicollinearity with GFA rather than a true inverse effect. These results demonstrate that public data can support practical, easily updated benchmarking, and suggest future gains from incorporating operational and climatic factors. - COLLAPSE
-
Analysis of Energy Usage Influencing Factors by Type of Medical Facility Using Public Data
-
Research Article
-
Descriptive Analysis of Energy Consumption in Korean Middle Schools
중학교 교육시설의 에너지 소비 특성에 관한 기술통계 분석
-
Hwang, Seok-Ho
황석호
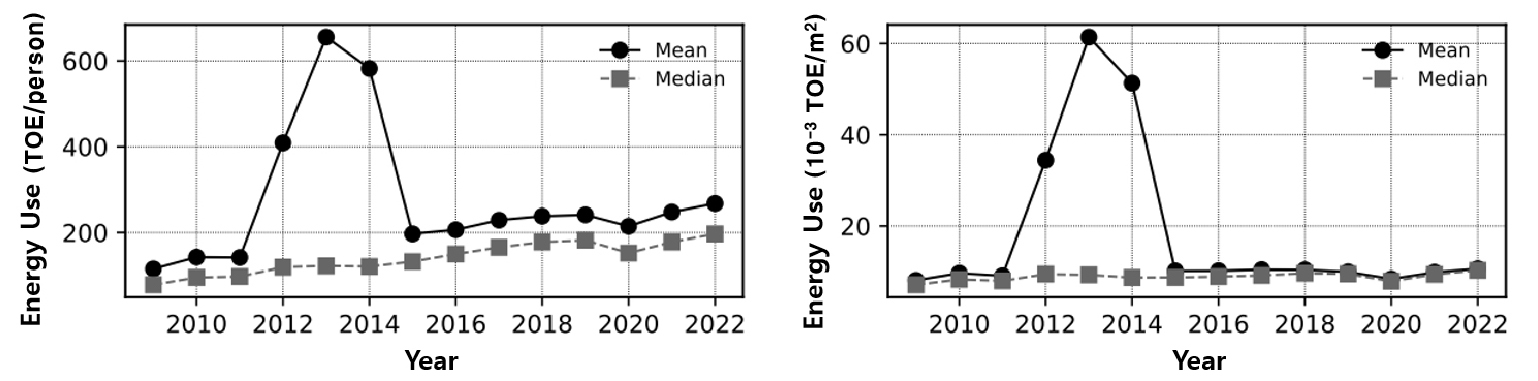
- This study examines energy use in Korean middle schools (2009~2022) using refined annual school-level panel data (~45,000 observations). We calculate total energy …
- This study examines energy use in Korean middle schools (2009~2022) using refined annual school-level panel data (~45,000 observations). We calculate total energy use, energy use per occupant, and energy use intensity (EUI), and assess distributions with mean, median, SD, IQR, histograms, and boxplots. Electricity dominated throughout (70~80%), with gas as a supplementary source (~15%), while heating/cooling areas expanded faster than total floor area, indicating deepening dependence on electricity-based systems. Scale effects emerged: smaller schools showed higher per-occupant use, whereas those exceeding 10,000 m² exhibited improved efficiency. The proportion of schools adopting renewables rose from 3.3% (2013) to 17.6% (2022), and the renewable share within adopting schools increased gradually. Leveraging a nationwide long-term panel, the study empirically identifies structural, regional, and scale-dependent patterns and provides baseline evidence to inform efficiency policies and support predictive modeling for sustainable school energy management. Regional variation is also observed, with certain provinces exhibiting consistently higher EUI levels than others. Because the renewable indicator reflects solar electricity in final-energy terms, it is not directly comparable to primary-energy-based installation mandates. - COLLAPSE
-
Descriptive Analysis of Energy Consumption in Korean Middle Schools
-
Research Article
-
An Experimental Analysis on the Possible Conservation of Domestic Hot Water Energy in Individual Heating Boiler using Mock-up
개별 난방 보일러의 급탕 에너지 절약 가능성에 대한 목업 기반의 실험적 분석
-
Jeong, Young-Sun, Kim, Yong-Ki, Oh, Suk-Joon
정영선, 김용기, 오석준
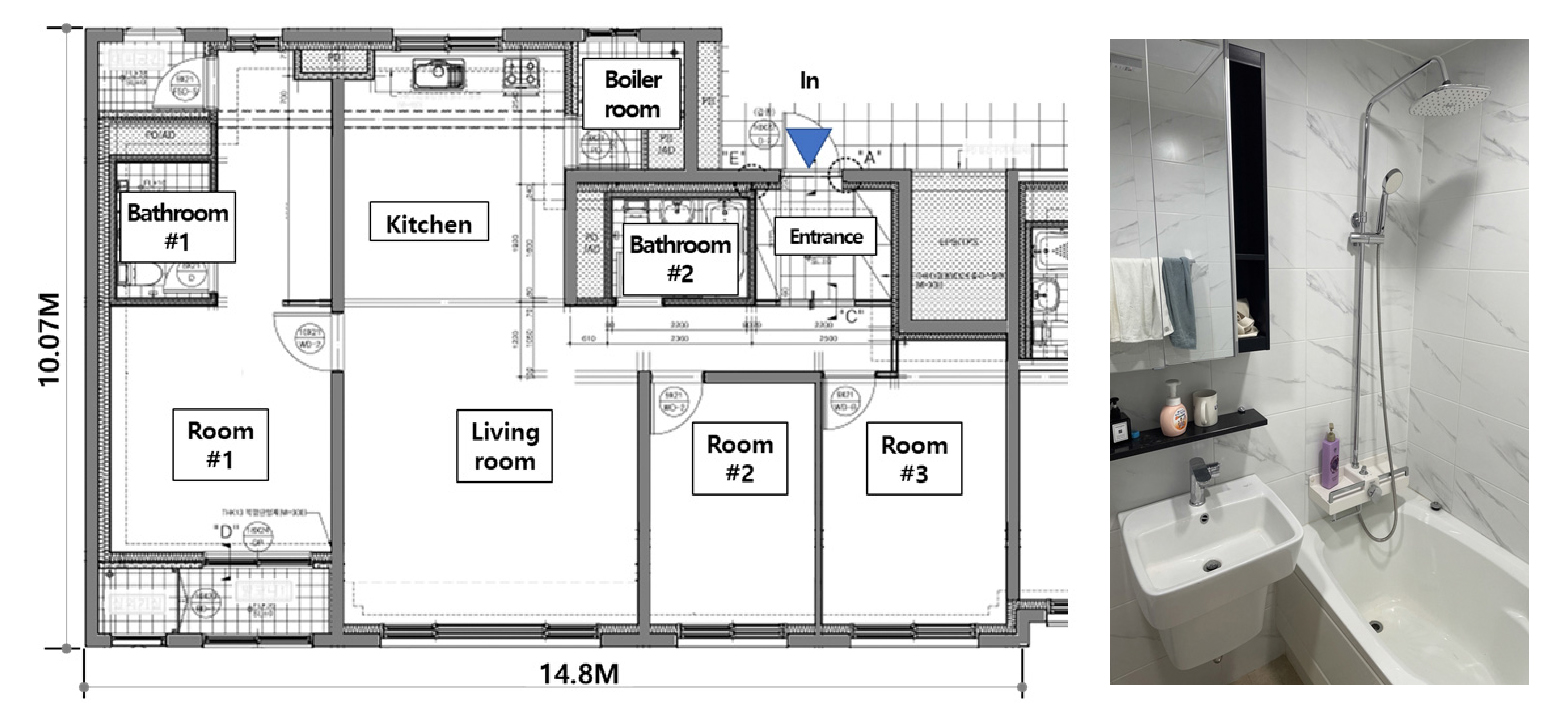
- The importance of domestic hot water energy in residential buildings is expected to continue increasing because of the upcoming mandatory of zero-energy …
- The importance of domestic hot water energy in residential buildings is expected to continue increasing because of the upcoming mandatory of zero-energy building. This study was conducted in mock-up laboratory to evaluate the potential of saving domestic hot water energy in individual heating boilers. The purpose of this study is to develop a hot water control method for individual heating boilers in the future based on this experimental results. The mock-up laboratory was simulated an 84 m² apartment housing unit. This study measured the hot water temperature at the end of the faucet and the shower head in bathroom and kitchen, the temperature of supply water to the boiler, the domestic hot water temperature and the flow rate provided from the boiler. In addition, the amount of LPG gas consumed by the operation of the boiler was measured. Each data was monitored at 1-second intervals. The first test was conducted for 5 days using hot water at the domestic hot water temperature setting values of 40℃. In the second test, we defined a 1-day hot water usage scenario and analyzed the savings by measuring energy consumption for domestic hot water based on LPG gas usage. The domestic hot water temperature setting values are 40℃ (case 1), 50℃ (case 2) and 60℃ (case 3). From this result, we were able to confirm the possibility of saving domestic hot water energy in individual heating boiler. - COLLAPSE
-
An Experimental Analysis on the Possible Conservation of Domestic Hot Water Energy in Individual Heating Boiler using Mock-up
-
Research Article
-
Numerical Evaluation of an Air-curtain Table for Indoor Aerosol Control
실내 에어로졸 제어를 위한 에어커튼 테이블의 수치적 평가
-
Park, Jeongan, Oh, Wonseok
박정안, 오원석
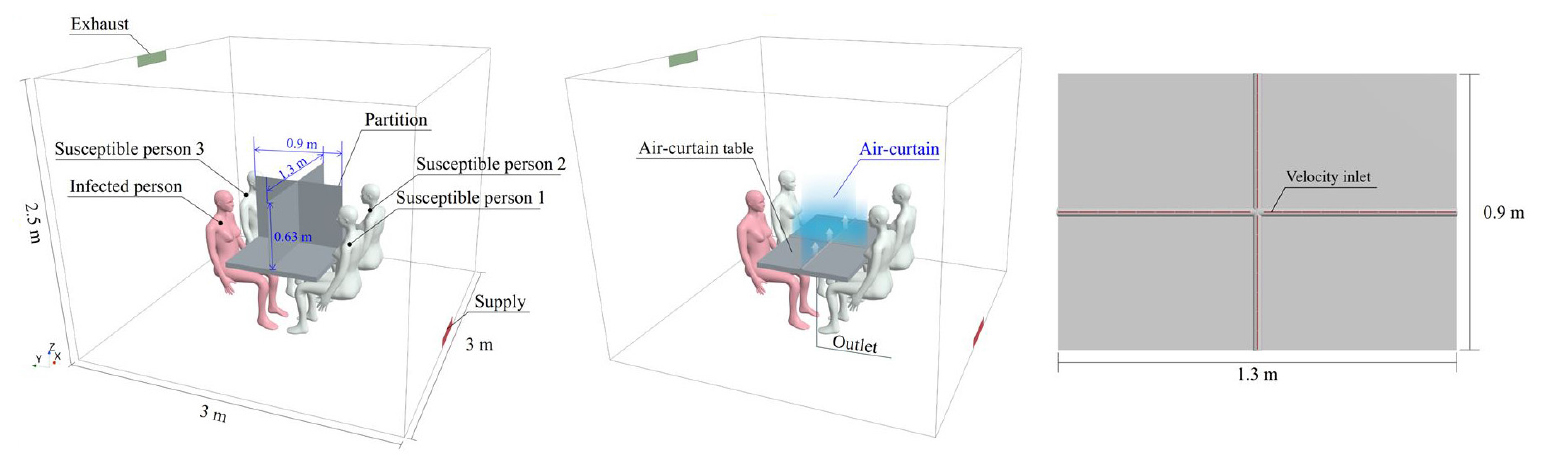
- The objective of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of an air-curtain table in reducing aerosol dispersion, a major transmission pathway …
- The objective of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of an air-curtain table in reducing aerosol dispersion, a major transmission pathway of respiratory infections in indoor environments. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulations were performed to assess and compare the aerosol reduction performance of air-curtain tables and partition walls under various table configurations and air-curtain supply flow rates. The results indicate that although partition walls altered the direct pathway of aerosol dispersion, they generated stagnant airflow zones within the breathing zone. In contrast, the air-curtain table effectively reduced aerosol dispersion by forming an upward airflow barrier that enhanced ventilation in the breathing zone and diluted contaminated air. Increasing the air-supply velocity further reduced the average indoor aerosol concentration by up to 92%, including approximately 34% reduction in the infected person’s breathing zone and more than 90% reduction for susceptible people. These findings highlight the potential of air-curtain tables as an effective indoor airflow control strategy for mitigating aerosol accumulation and reducing infection risks in enclosed environments. - COLLAPSE
-
Numerical Evaluation of an Air-curtain Table for Indoor Aerosol Control
-
Research Article
-
Energy Benefit of Air-Conditioning System Based on Central Air Source Heat Pump in Office Buildings
사무소 건물의 중앙 열원 공급식 공기열 히트펌프 냉난방 시스템의 에너지 절감 가능성 분석
-
Lee, Soo-Jin, Park, Min-Geon, Hong, Su-Yeon, Choi, Min-Young, Jeong, Jae-Weon
이수진, 박민건, 홍수연, 최민영, 정재원
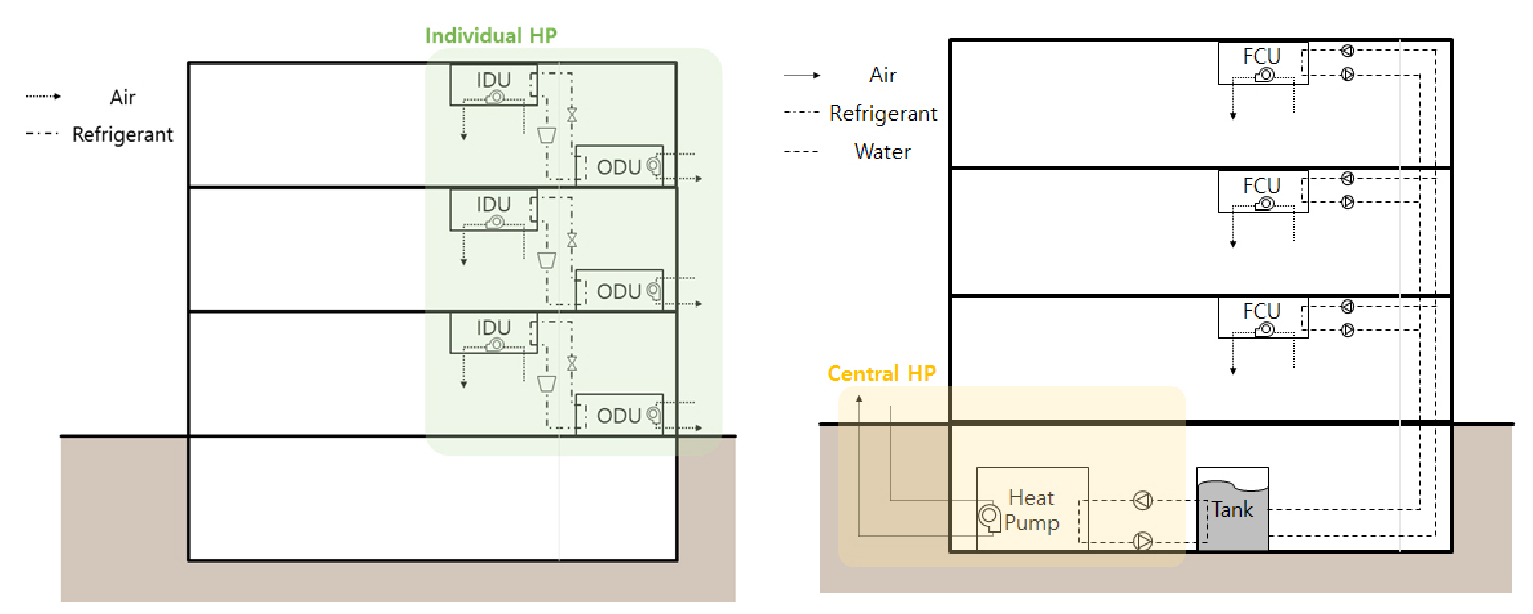
- This study proposes and evaluates an air-conditioning system for office buildings that utilizes a central air-source heat pump (ASHP) to supply heating …
- This study proposes and evaluates an air-conditioning system for office buildings that utilizes a central air-source heat pump (ASHP) to supply heating and cooling water to individual heat pumps. The proposed system aims to overcome the limitations of conventional decentralized air-to-air heat pumps, whose performance varies significantly with outdoor air temperature. To assess its performance, a thermodynamic cycle analysis and annual energy simulation were conducted using TRNSYS 18 and Engineering Equation Solver (EES) program, considering a typical office building model. Results show that the proposed system achieved higher isentropic efficiency for both individual and central heat pumps, with values of approximately 0.66 and 0.80, respectively, due to the reduced compression ratio. The coefficient of performance (COP) of the individual heat pumps in the proposed system improved by about 45% compared to the conventional system, reaching an average COP of 5.77. Moreover, the total annual energy consumption of the proposed system, including the central unit and circulation pumps, was approximately 99.4 MWh, which represents an 18% reduction compared to the reference central system (115.29 MWh). These findings indicate that the proposed central-source integrated ASHP system can significantly enhance overall energy efficiency by stabilizing heat source temperatures and optimizing the operation of distributed heat pumps. - COLLAPSE
-
Energy Benefit of Air-Conditioning System Based on Central Air Source Heat Pump in Office Buildings
-
Research Article
-
Development of Cooling Energy Reduction Algorithm for Optimal Control of Chilled and Condenser Water in WSE
Water-side economizer 시스템의 냉수 및 냉각수 최적 제어를 위한 냉방 에너지 절감 알고리즘 개발
-
Go, Su-Min, Kim, Su-Ji, Song, Young-Hak
고수민, 김수지, 송영학
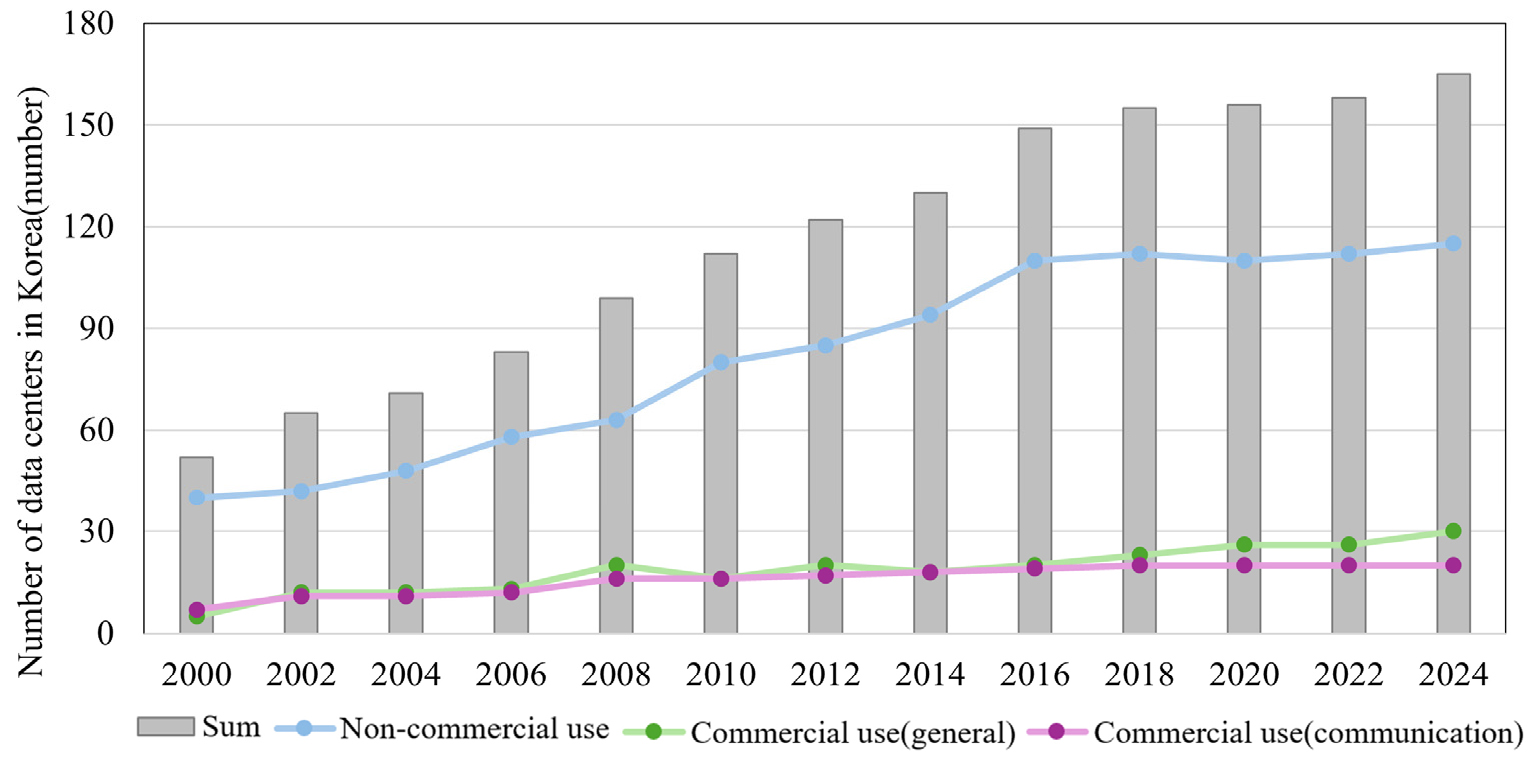
- This study aims to develop and quantitatively verify the effectiveness of an optimal control algorithm for a Water-side Economizer (WSE) system to …
- This study aims to develop and quantitatively verify the effectiveness of an optimal control algorithm for a Water-side Economizer (WSE) system to reduce cooling energy consumption in data centers. Optimal fluid combinations that minimize energy usage for each outdoor wet-bulb temperature were derived using a combined LSTM and LightGBM model. An algorithm for the optimal operation of chilled water and condenser 1, 2 water, including the selection of the most appropriate optimal fluid combination, was developed and applied to the WSE system. Comparative analysis between the model with the optimal control algorithm and the Base model revealed that the optimized model enhanced operational stability by precisely and regularly controlling the temperatures of the chilled water and cooling water. Furthermore, the Free cooling operation period increased by approximately 11.8% compared to the conventional operation, while the Chiller cooling operation period decreased by 23.4%, resulting in reduced overall system energy consumption and lowering the peak load from 180 kW to 160 kW. These results confirm that the optimal operation of chilled water and cooling water contributes to cooling energy savings and improved system efficiency in data centers. - COLLAPSE
-
Development of Cooling Energy Reduction Algorithm for Optimal Control of Chilled and Condenser Water in WSE
-
Research Article

-
An Empirical Study on the Effects of ‘Targeted Airtightness Reinforcement’ on Reducing Inter-unit Airborne Sound
‘취약부 기밀 보강’의 세대 간 공기전달 소음 저감 효과에 관한 실증 연구
-
Park, Jong-Il, Kim, Min-Ju, Jeong, Su-Gwang
박종일, 김민주, 정수광
- This study aimed to empirically validate reduction methods for inter-floor noise, a critical residential issue in apartment buildings, specifically focusing on airborne …
- This study aimed to empirically validate reduction methods for inter-floor noise, a critical residential issue in apartment buildings, specifically focusing on airborne sound transmitted through gaps such as pipe ducts. A “targeted airtightness reinforcement” intervention was implemented on bathroom pipe ducts and electrical inlets within a single unit in an actual living environment (Living Lab). The airtightness performance (n50) of the entire unit and the inter-floor airborne sound insulation performance (D) of two bathrooms were measured and compared before and after the intervention, in accordance with KS F ISO 16283-1. The results indicated that the airtightness performance of the entire unit showed a marginal improvement of approximately 2.3%, changing from 2.20 ACH before construction to 2.15 ACH after construction. In contrast, the sound insulation performance improved by 1.9 dB (from 50.3 dB to 52.2 dB) in the master bedroom bathroom and by 1.2 dB (from 49.5 dB to 50.7 dB) in the secondary bedroom bathroom. These findings suggest that reinforcing “local acoustic weak points,” which serve as key noise transmission paths, yields substantial and significant effects on inter-floor noise reduction, even with minimal changes to the overall airtightness of the unit. - COLLAPSE
-
An Empirical Study on the Effects of ‘Targeted Airtightness Reinforcement’ on Reducing Inter-unit Airborne Sound
-
Research Article
-
A Comparative Life Cycle Assessment of Building Insulation Materials Complying with Korean Insulation and Fire Safety Standards
국내 단열·화재안전 기준을 만족하는 건축용 단열재의 전과정평가(LCA) 비교 연구
-
Kang, Chan-Hyeok, Jung, Bo-Kyung, Kwon, Young-Cheol
강찬혁, 정보경, 권영철
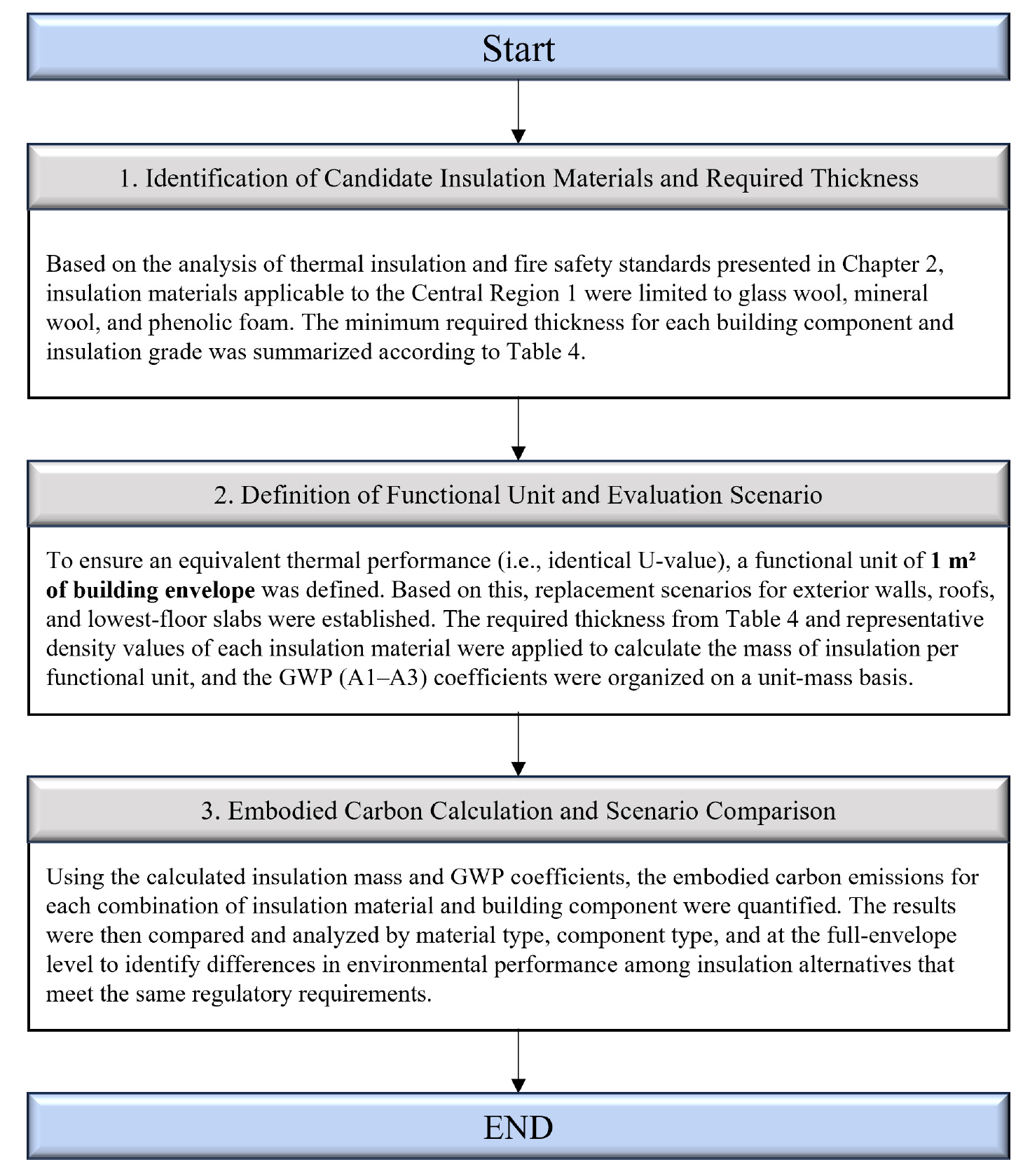
- This study evaluates the embodied carbon of insulation materials that comply with Korean reinforced insulation and fire safety standards. Glass wool, mineral …
- This study evaluates the embodied carbon of insulation materials that comply with Korean reinforced insulation and fire safety standards. Glass wool, mineral wool, and phenolic foam were assessed using EPD-based GWP values and the minimum insulation thickness required for the Central Region 1 zone to identify environmentally preferable options. As regulations become more stringent, the role of insulation in reducing whole-life carbon has become increasingly important in design practice. This study therefore provides a detailed comparison of material-specific embodied carbon differences across exterior walls, roofs, and floor assemblies. In addition, the analysis considers how required thickness and density interact to influence embodied carbon outcomes across different building envelope conditions. The findings offer practical insight for architects and policymakers seeking to balance regulatory compliance with environmental performance. The results show that glass wool yields the lowest embodied carbon, while mineral wool shows the highest due to greater density and material use. Phenolic foam demonstrates mid-level emissions despite of reduced thickness from its low thermal conductivity. These findings indicate that meeting only insulation and fire regulations is insufficient, highlighting the need for LCA-based insulation selection to reduce embodied carbon and support more sustainable building practices. - COLLAPSE
-
A Comparative Life Cycle Assessment of Building Insulation Materials Complying with Korean Insulation and Fire Safety Standards
-
Research Article
-
Improving Monthly Energy Demand Calculations through Area-Normalized 1D and 2D Thermal Bridges
1D·2D 열교의 면적기반 환산을 적용한 월간법 에너지요구량 평가 개선 연구
-
Lim, Su-Hyun, Jun, Min-Seok
임수현, 전민석
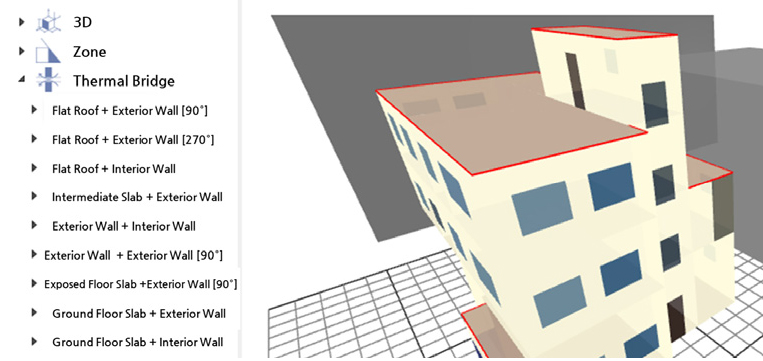
- This study presents an area-based framework for incorporating one-dimensional (1D) and two- dimensional (2D) thermal bridges into monthly energy-demand calculations. Traditional single …
- This study presents an area-based framework for incorporating one-dimensional (1D) and two- dimensional (2D) thermal bridges into monthly energy-demand calculations. Traditional single correction factors do not capture variations in thermal-bridge geometry or construction details, leading to inaccuracies in heat-loss estimates. The proposed method quantifies 1D thermal bridges as area-normalized transmittance increments (ΔU1D) and 2D thermal bridges as ψ·l/A, enabling consistent evaluation of thermal-bridge effects across walls, roofs, and floors. A 3D model–based automatic extraction of junction lengths further improves computational accuracy and practical applicability. The framework aligns with ISO 52016-1 procedures and is expected to support future developments in automated and 3D Model-integrated thermal-bridge assessment. - COLLAPSE
-
Improving Monthly Energy Demand Calculations through Area-Normalized 1D and 2D Thermal Bridges
-
Research Article
-
GHG Mitigation Pathway Scenarios for Metropolitan Governments under an Equality-Based Carbon Budget in the Building Sector
건물부문 평등주의 탄소예산 적용을 통한 광역지자체별 온실가스 감축경로 시나리오
-
Kim, Yu-Min
김유민
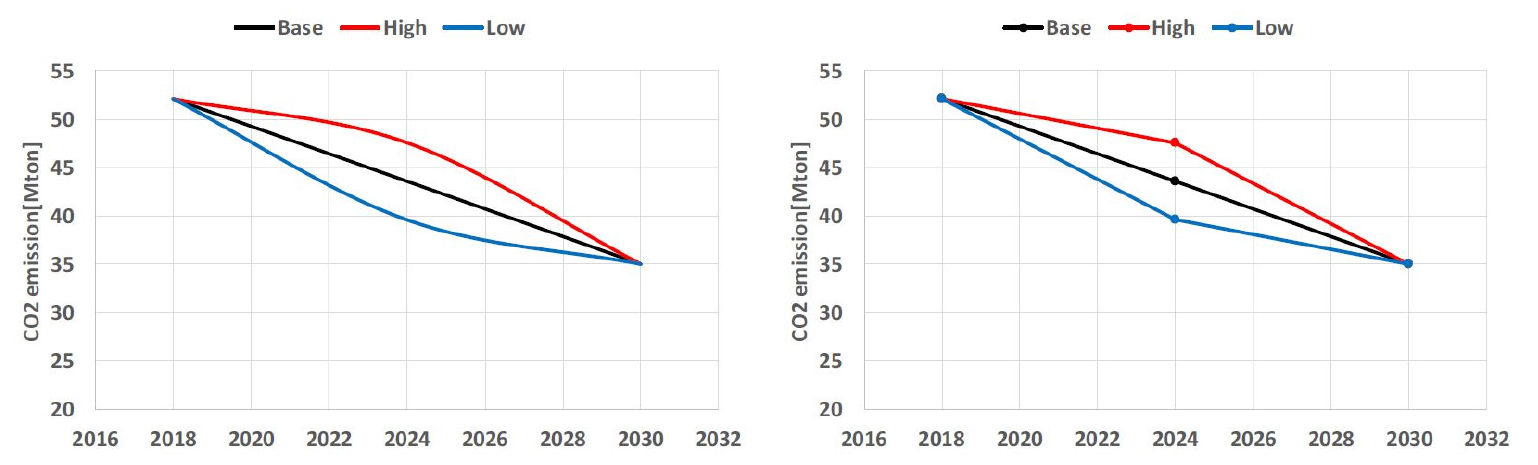
- This study proposes a methodology for designing equality-based carbon budget pathways for the building sector across Korea’s 17 metropolitan governments, grounded in …
- This study proposes a methodology for designing equality-based carbon budget pathways for the building sector across Korea’s 17 metropolitan governments, grounded in the 2030NDC and the 2050 carbon neutrality scenario. National annual emission targets for the building (direct and indirect) and transformation sectors are interpreted as a 2018–2030 carbon budget, with missing years linearly interpolated. Current allocation practice is represented as a grandfathering principle, after which an egalitarian (population-share) principle is introduced to construct adjusted scenarios with convergence years in 2030, 2040, and 2050. National trajectories are approximated using a piecewise-linear pathway with a single turning point (direct: 2026; indirect: 2028), from which annual reduction slopes and local carbon budgets are derived. Results indicate that high per-capita emitting regions face steeper and earlier reductions under the egalitarian framework, while more populous regions experience a relative easing of reduction burdens. For the direct building sector under convergence in 2030, Seoul’s 2030 target decreases from 7.59 to 6.21 MtCO2, whereas Gyeonggi-do’s increases from 7.39 to 9.74 MtCO2. In addition, Seoul’s required annual reduction rate increases from 192 to 347 ktCO2/yr up to the 2026 turning point and from 542 to 577 ktCO2/yr thereafter, illustrating the front-loaded mitigation implied by egalitarian convergence. The proposed framework supports consistent target setting between national and local levels and provides a transparent basis for integrating alternative equity principles in future studies. - COLLAPSE
-
GHG Mitigation Pathway Scenarios for Metropolitan Governments under an Equality-Based Carbon Budget in the Building Sector
-
Research Article
-
Simulation Study on Heating Energy of Apartment Buildings using Actual Weather Data
실제 기상데이터를 활용한 공동주택 난방 에너지 시뮬레이션 연구
-
Rhee, Kyu-Nam, Jung, Gun-Joo
이규남, 정근주
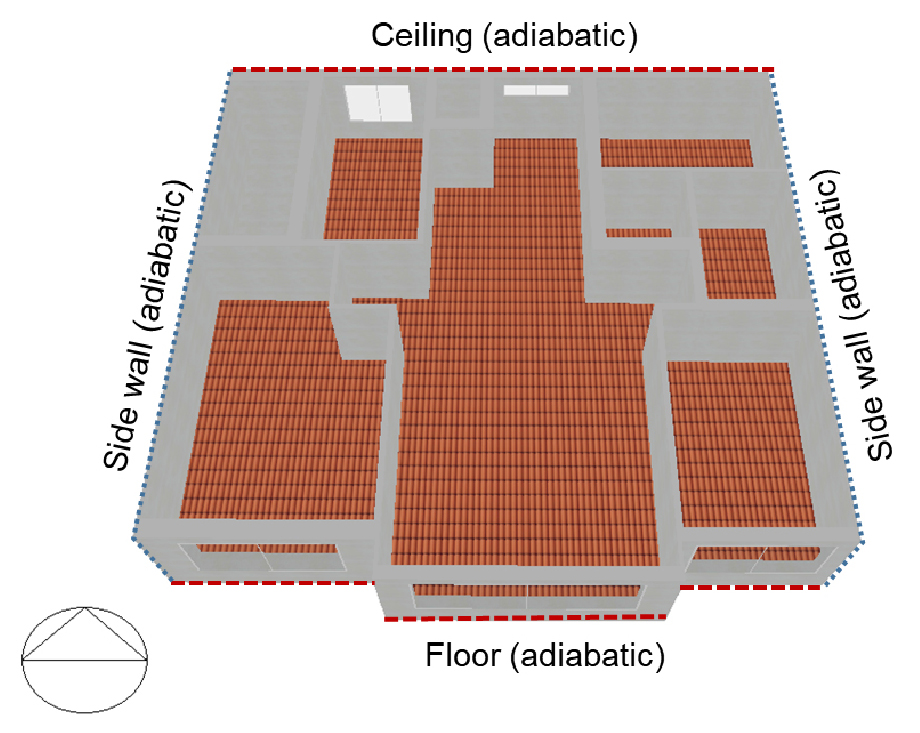
- Typical meteorological year (TMY) data is widely used to predict building energy performance under standardized climate conditions. However, the TMY data may …
- Typical meteorological year (TMY) data is widely used to predict building energy performance under standardized climate conditions. However, the TMY data may not be suitable for assessing the energy performance under climate conditions of a specific year. This study was conducted to investigate the impact of TMY and actual weather data (AWD) on the heating energy consumption of apartment buildings. Compared to the actual energy consumption, the TMY-based simulation resulted in the error up to –15.3% and –14.6% for Seoul and Busan, respectively. In contrast, the AWD-based simulation showed the error of –1.7%~+8.9% and –3.7%~+2.9% for Seoul and Busan, respectively. It was also suggested that the TMY-based model should be modified using average winter temperature and heating degree days. The modified TMY model showed the discrepancy up to 8.2% and 8.8% for Seould and Busan, respectively, compared to the results by the AWD-based simulation. - COLLAPSE
-
Simulation Study on Heating Energy of Apartment Buildings using Actual Weather Data
-
Research Article
-
Preliminary Energy Performance Evaluation of Apartment Buildings Using Energy Consumption Heatmaps
공동주택 에너지 사용량 히트맵을 활용한 사전 에너지 성능평가
-
Shin, Ji-Hyun, Song, Suwon
신지현, 송수원
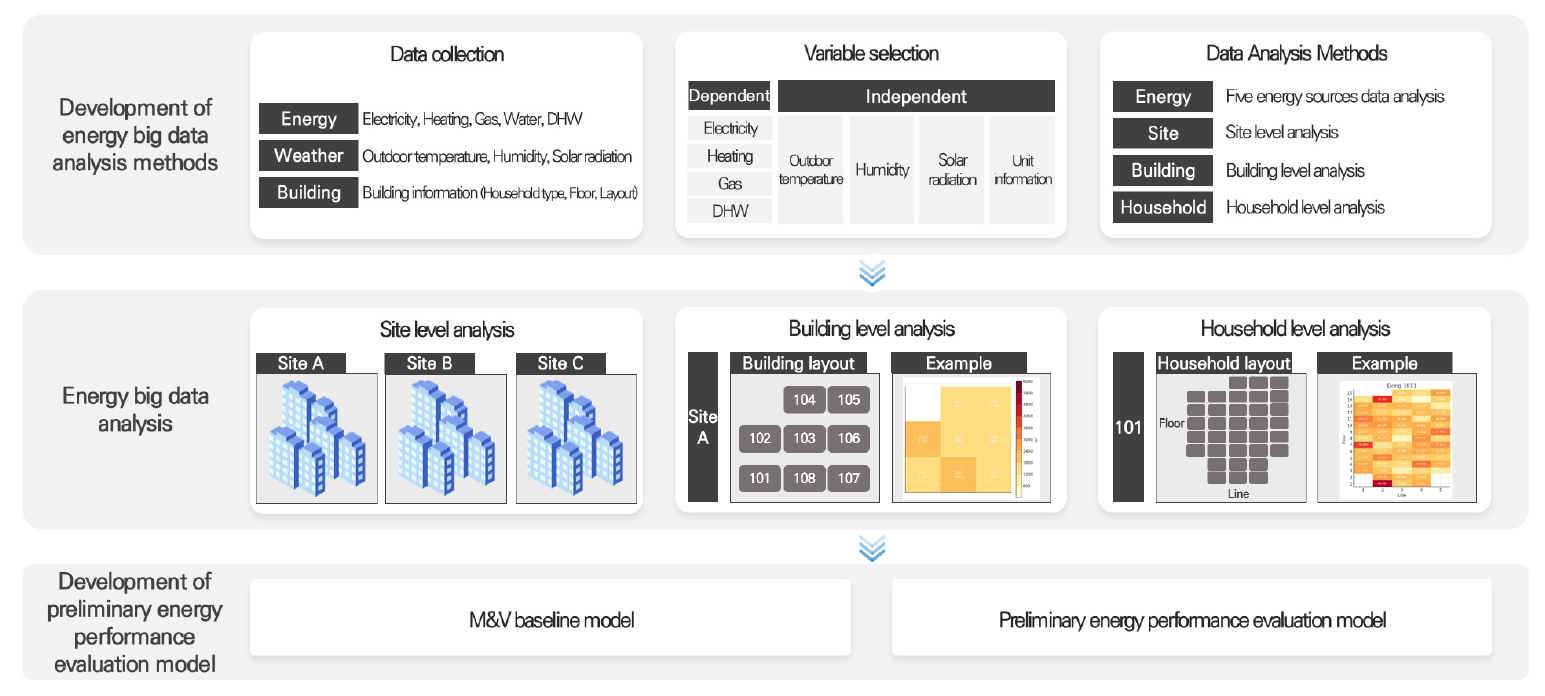
- This study proposes a data-driven framework for the preliminary energy performance evaluation of apartment buildings using energy consumption heatmaps derived from measured …
- This study proposes a data-driven framework for the preliminary energy performance evaluation of apartment buildings using energy consumption heatmaps derived from measured data. Electricity and heating energy use were first analyzed at both the building and household levels in a apartment complex, and heatmap visualization was then applied to identify the spatial variability of energy-intensive areas within the complex. The results show that substantial differences in energy consumption exist not only among buildings within the same complex but also among households within the same building. Based on the identified energy use characteristics, Measurement and Verification (M&V) baseline models that meet the acceptable criteria of ASHRAE Guideline 14 were developed to estimate potential energy savings for selected energy-intensive buildings and households. Consequently, the proposed framework provides a quantitative basis for identifying priority targets for energy efficiency improvements in apartment buildings prior to the implementation of energy conservation measures (ECMs). - COLLAPSE
-
Preliminary Energy Performance Evaluation of Apartment Buildings Using Energy Consumption Heatmaps
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of Korean Institute of Architectural Sustainable Environment and Building Systems
Journal of Korean Institute of Architectural Sustainable Environment and Building Systems
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of Korean Institute of Architectural Sustainable Environment and Building Systems
Journal of Korean Institute of Architectural Sustainable Environment and Building Systems











